Interfacing to the Analog World problems
- 1. One major difference between a counter-ramp A/D converter and a successive-approximation converter is:
Options- A. the counter-ramp A/D converter is much faster than the successive-approximation converter
- B. with the successive-approximation converter the final binary result is always slightly less than the equivalent analog input, whereas with the counter-ramp A/D converter it is slightly more
- C. with the successive-approximation converter the final binary result is always slightly more than the equivalent analog input, whereas with the counter-ramp A/D converter it is slightly less
- D. none of the above Discuss
Correct Answer: with the successive-approximation converter the final binary result is always slightly less than the equivalent analog input, whereas with the counter-ramp A/D converter it is slightly more
- 2. What is the main disadvantage of the stairstep-ramp A/D converter?
Options- A. The counter must count up from zero at the beginning of each conversion sequence, and the conversion time will vary depending on the input voltage.
- B. It requires a counter.
- C. It requires a precision clock in order for the conversion to be reliable.
- D. All of the above Discuss
Correct Answer: The counter must count up from zero at the beginning of each conversion sequence, and the conversion time will vary depending on the input voltage.
- 3. One disadvantage of the tracking A/D converter is:
Options- A. that it requires two counters?one for up and one for down.
- B. that the binary output will oscillate between two binary states when the analog input is constant.
- C. the need for an accurate clock reference for the counter.
- D. the need for a latch and its associated control circuit. Discuss
Correct Answer: that the binary output will oscillate between two binary states when the analog input is constant.
- 4. What is the current in the feedback resistor for the circuit given below?
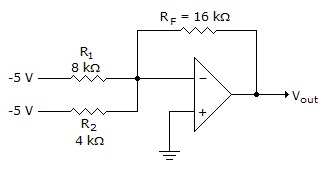
Options- A. 0.625 mA
- B. 1.25 mA
- C. 1.875 mA
- D. 1.625 mA Discuss
Correct Answer: 1.875 mA
- 5. What is the main disadvantage of the counter-ramp A/D converter?
Options- A. It requires a counter.
- B. The counter must count up from zero at the beginning of each conversion sequence, and the conversion time will vary depending on the input voltage.
- C. It requires a precision clock in order for the conversion to be reliable.
- D. The counter must count up from zero at the beginning of each conversion sequence, and the conversion time will vary depending on the input voltage. It requires a precision clock in order for the conversion to be reliable. Discuss
Correct Answer: The counter must count up from zero at the beginning of each conversion sequence, and the conversion time will vary depending on the input voltage.
- 6. What is the accuracy of a D/A converter?
Options- A. It is the reciprocal of the number of discrete steps in the D/A output.
- B. It is the comparison between the actual output of the converter and its expected output.
- C. It is the converter's ability to resolve between forward and reverse steps when sequenced over its entire range of inputs.
- D. It is the deviation between the ideal straight-line output and the actual output of the converter. Discuss
Correct Answer: It is the comparison between the actual output of the converter and its expected output.
- 7. What is the major advantage of the R/2R ladder D/A converter as compared to a binary-weighted D/A converter?
Options- A. It has fewer parts for the same number of inputs.
- B. It is much easier to analyze its operation.
- C. It uses only two different resistor values.
- D. The virtual ground is eliminated and the circuit is therefore easier to understand and troubleshoot. Discuss
Correct Answer: It uses only two different resistor values.
- 8. An analog-to-digital converter has a four-bit output. How many analog values can it represent?
Options- A. 4
- B. 1/4
- C. 16
- D. 0.0625 Discuss
Correct Answer: 16
- 9. What is the maximum output voltage for the circuit shown below?
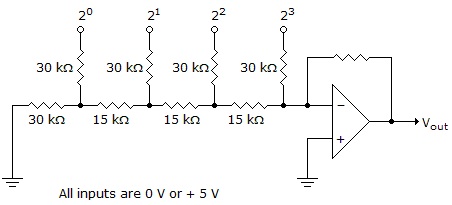
Options- A. ?20 volts
- B. ?5 volts
- C. ?9.375 volts
- D. ?2.1775 volts Discuss
Correct Answer: ?9.375 volts
- 10. If the range of output voltage of a 6-bit DAC is 0 to 15 volts, what is the step voltage of the output?
Options- A. 0.117 volt/step
- B. 0.234 volt/step
- C. 2.13 volts/step
- D. 4.26 volts/step Discuss
Correct Answer: 0.234 volt/step
More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
