Railways problems
- 1. According to Railway Board, no diamond crossing should be flatter than
Options- A. 1 in 6
- B. 1 in
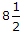
- C. 1 in 12
- D. 1 in 16 Discuss
Correct Answer: 1 in
- 2. Coning of wheels is provided
Options- A. to check lateral movement of wheels
- B. to avoid damage to inner faces of rails
- C. to avoid discomfort to passengers
- D. All the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: All the above.
- 3. Regional Indian railways use different types of sleepers according to their
Options- A. availability
- B. economy
- C. suitability
- D. design
- E. all the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: all the above.
- 4. Minimum length of a transition curve required for
Options- A. 2° curves for a maximum permissible speed of 135 km/hr, is 220 metres
- B. 4° curves for a maximum permissible speed of 95 km/hr, is 220 metres
- C. 6° curves for a maximum permissible speed of 80 km/hr, is 220 metres
- D. All the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: All the above.
- 5. Heel of crossing is the line joining
Options- A. ends of splice rail and point rail
- B. ends of lead rails butting the crossing
- C. ends of wing rails
- D. throat and actual nose of crossing. Discuss
Correct Answer: ends of splice rail and point rail
- 6. The spread between the point and splice rails at a distance of 4.25 rn is 50 cm. The size of the crossing is
Options- A. 1 in 6
- B. 1 in
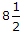
- C. 1 in 12
- D. 1 in 16 Discuss
Correct Answer: 1 in
- 7. By interchanging gibs and cotters of a pot sleeper, gauge may be slackened by
Options- A. 1.2 mm
- B. 2.2 mm
- C. 3.2 mm
- D. 4.2 mm
- E. 5.0 mm Discuss
Correct Answer: 3.2 mm
- 8. A mono-block sleeper has
Options- A. square section
- B. rectangular section
- C. trapezoidal section
- D. semi-circular section
- E. none of these. Discuss
Correct Answer: trapezoidal section
- 9. For providing the required tilt of rails, adazing of wooden sleepers, is done for
Options- A. bull headed rails
- B. double headed rails
- C. flat footed rails
- D. any type of rails
- E. none of these. Discuss
Correct Answer: flat footed rails
- 10. The standard dimensions of a wooden sleeper for M.G. railway track are
Options- A. 2.74 m x 25 cm x 13 cm
- B. 1.83 m x 20 cm x 11 cm
- C. 1.52 m x 15 cm x 10 cm
- D. 1.75 m x 20 cm x 12 cm
- E. none of these. Discuss
Correct Answer: 1.83 m x 20 cm x 11 cm
More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
