Railways problems
- 1. Bull headed rails are generally provided on
Options- A. points and crossing
- B. straight tangents
- C. curved tracks
- D. metre gauge tracks
- E. none of these. Discuss
Correct Answer: points and crossing
- 2. The distance between theoretical nose of crossing and actual nose of crossing for practical purposes, is
Options- A. Nose thickness x tan ?
- B. Nose thickness x cot ?
- C. Nose thickness x sin ?
- D. Nose thickness x cos ? Discuss
Correct Answer: Nose thickness x cot ?
- 3. The main advantage of a long rail over short one, is
Options- A. it requires less number of rail fastenings
- B. it provides smooth running of trains
- C. it involves less maintenance cost
- D. it provides conform to passengers
- E. all the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: all the above.
- 4. An extra 7.5 cm ballast width is not provided on outer side on a curve, if its degree is
Options- A. 6°
- B. 5°
- C. 4°
- D. 3°
- E. 2° Discuss
Correct Answer: 3°
- 5. Pick up the incorrect statement from the following:
Options- A. Ends of adjoining rails should be in true alignment
- B. Rail joints should be as strong as the rail section itself
- C. Rail joints should be elastic laterally as well as vertically
- D. Ends of adjoining rails butt against to give a continuity
- E. All the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: All the above.
- 6. The gradient on which an additonal engine is required to negotiate the gradient, is called
Options- A. momentum gradient
- B. pusher gradient
- C. ruling gradient
- D. steep gradient. Discuss
Correct Answer: pusher gradient
- 7. If D is distance between centres of two parallel tracks of gauge G with entire curved leads and equal angles of crossing, total length of crossover, is
Options- A. D (4R - 2G - D)
- B. D (3R - 2G -D)
- C. D (3R + 2G - D)
- D. D (4 + 2G - D) Discuss
Correct Answer: D (4R - 2G - D)
- 8. The lengths of the standard crossings in India for Broad gauge and Metre gauge tracks is same for
Options- A. 1 in
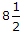 B.G. and, in 12 M.G.
B.G. and, in 12 M.G. - B. 1 in 12 B.G. and, 1 in 16 M.G.
- C. 1 in 12 B.G. and 1 in
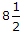 M.G.
M.G. - D. 1 in 16 B.G. and 1 in 12 M.G. Discuss
Correct Answer: 1 in
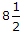 B.G. and, in 12 M.G.
B.G. and, in 12 M.G. - 9. Cast iron sleeper, is
Options- A. pot sleeper
- B. box sleeper
- C. Duplex sleeper
- D. plate sleeper
- E. All the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: All the above.
- 10. In permanent way, ballast
Options- A. transfers load from sleepers to the formation
- B. provides an elastic bed to the track
- C. provides a drainage of track
- D. all the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: all the above.
More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
