Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Interfacing to the Analog World See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The output of the circuit in the given figure (a) at point X on figure (b) will be ________.

Options- A. 1.011 V
- B. 2.75 V
- C. ?1.011 V
- D. ?2.75 V
- Correct Answer
- ?2.75 V
- 1. Which of the equations below expresses the voltage gain relationship for an operational amplifier?
Options- A. Vout = Vin/Av
- B. Vout/Vin = Rout/Rin
- C. Vin/Vout = Rout/Rin
- D. Vout/Vin = ?Rf/Rin Discuss
- 2. An actuator is usually a device that:
Options- A. converts analog data to meaningful digital data.
- B. controls a physical variable.
- C. stores digital data and then processes that data according to a set of specified instructions.
- D. converts a physical variable to an electrical variable. Discuss
- 3. What function does the CTR DIV 8 circuit given below perform?
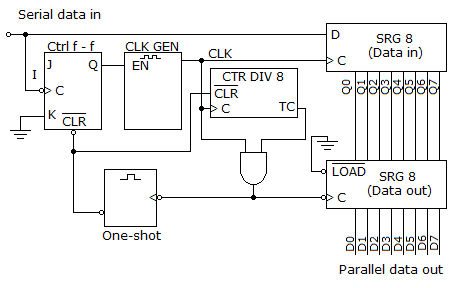
Options- A. It divides the clock frequency down to match the frequency of the serial data in.
- B. The divide-by-8 counter is triggered by the control flip-flop and clock, which then allows the data output register to begin storing the input data. Once all eight data bits are stored in the data output register, the data output register and the divide-by-8 counter trigger the one-shot. The one-shot then begins the process all over again.
- C. The divide-by-8 counter is used to verify that the parity bit is attached to the input data string.
- D. It keeps track of the eight data bits, triggering the transfer of the data through the output register and the one-shot, which then resets the control flip-flop and divide-by-8 counter. Discuss
- 4. Regardless of whether you develop a description in AHDL or VHDL, the circuit's proper operation can be verified using a ________.
Options- A. PROCESS
- B. computer
- C. simulator
- D. primitive library Discuss
- 5. The ________ circuit overcomes the problem of switching caused by jitter on the inputs.
Options- A. astable multivibrator
- B. monostable multivibrator
- C. bistable multivibrator
- D. Schmitt trigger Discuss
- 6. What type of DAC is shown below?
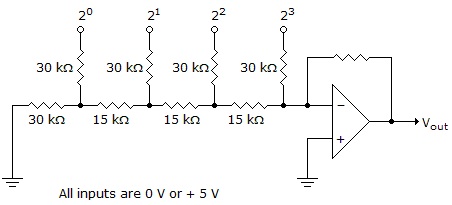
Options- A. binary-weighted
- B. R-2R ladder Discuss
- 7. What is the conversion time of a flash converter?
Options- A. 20 µs
- B. 10 µs
- C. 1 µs
- D. The conversion takes place continuously. Discuss
- 8. The purpose of a pull-up resistor is to keep a terminal at a ________ level when it would normally be at a ________ level.
Options- A. LOW, float
- B. HIGH, float
- C. clock, float
- D. pulsed, float Discuss
- 9. Sample-and-hold circuits in A/D converters are designed to:
Options- A. sample and hold the output of the binary counter during the conversion process
- B. stabilize the comparator's threshold voltage during the conversion process
- C. stabilize the input analog signal during the conversion process
- D. sample and hold the D/A converter staircase waveform during the conversion process Discuss
- 10. Why does the data sheet for the 7476 only give a minimum value for the clock pulse width (both HIGH and LOW)?
Options- A. nominal value
- B. best-case condition
- C. worst-case condition Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: Vout/Vin = ?Rf/Rin
Correct Answer: controls a physical variable.
Correct Answer: It keeps track of the eight data bits, triggering the transfer of the data through the output register and the one-shot, which then resets the control flip-flop and divide-by-8 counter.
Correct Answer: simulator
Correct Answer: Schmitt trigger
Correct Answer: R-2R ladder
Correct Answer: The conversion takes place continuously.
Correct Answer: HIGH, float
Correct Answer: stabilize the input analog signal during the conversion process
Correct Answer: worst-case condition
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
