Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) problems
- 1. A transistor used in a digital circuit will have two operating states, which are cutoff and saturation.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
- 2. BJTs are "junction" transistors because they use current-carrying P-N junctions.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
- 3. The voltage measured from the collector to the emitter is the sum of the voltage base-emitter plus the voltage collector-base.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
- 4. Current gain in a transistor is inversely proportional to collector current.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: False
- 5. The three bipolar transistor circuit configurations are common-base, common-emitter, and emitter-follower.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
- 6. When a transistor is operating as a variable resistor it has transistance.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
- 7. The polarity of VBE is such that it reverse biases the base-emitter junction.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: False
- 8. The voltage gain of a transistor is inversely proportional to the change in output current.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
- 9. This is a PNP transistor.
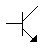
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: False
- 10. The voltage measured from the collector to the emitter is the sum of the base-emitter voltage plus the collector-base voltage.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
