Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Counters Comments
- Question
A glitch that appears on the decoded output of a ripple counter is often difficult to see on an oscilloscope because ________.
Options- A. it is a random event
- B. it occurs less frequently than the normal decoded output
- C. it is very fast
- D. all of the above
- Correct Answer
- all of the above
- 1. A reliable method for eliminating decoder spikes is the technique called ________.
Options- A. strobing
- B. feeding
- C. wagging
- D. waving Discuss
- 2. Assume a 4-bit ripple counter has a failure in the second flip-flop such that it "locks up." The third and fourth stages will ________.
Options- A. continue to count with correct outputs
- B. continue to count but have incorrect outputs
- C. stop counting
- D. turn into molten silicon Discuss
- 3. Asynchronous counters are often called ________ counters.
Options- A. toggle
- B. ripple
- C. binary
- D. flip-flop Discuss
- 4. Assume you want to determine the timing diagram for a 4-bit counter using an oscilloscope. The best choice for an oscilloscope trigger signal is ________.
Options- A. the most significant bit (MSB)
- B. the least significant bit (LSB)
- C. the clock signal
- D. from a composite of the MSB and LSB Discuss
- 5. The technique used by one-shots to respond to an edge rather than a level is called ________.
Options- A. level management
- B. edge triggering
- C. trigger input
- D. edge trapping Discuss
- 6. Shift-register counters use ________, which means that the output of the last FF in the register is connected back to the first FF in some way.
Options- A. MOD
- B. feedback
- C. strobing
- D. switchbacks Discuss
- 7. A 4-bit binary up counter has an input clock frequency of 20 kHz. The frequency of the most significant bit is ________.
Options- A. 1.25 kHz
- B. 2.50 kHz
- C. 160 kHz
- D. 320 kHz Discuss
- 8. The given circuit is a(n) ________.
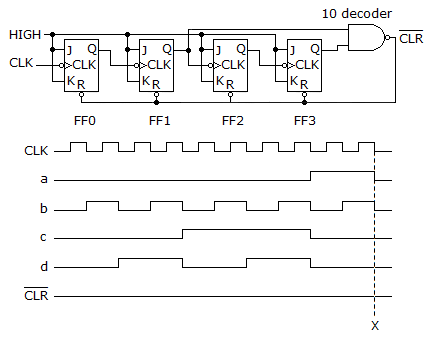
Options- A. three-bit synchronous binary counter
- B. eight-bit asynchronous binary flip-flop
- C. two-bit asynchronous binary counter
- D. four-bit asynchronous binary counter Discuss
- 9. The MOD-10 counter is also referred to as a ________ counter.
Options- A. decade
- B. strobing
- C. BCD
- D. circuit Discuss
- 10. In order to use a shift register as a counter, ________.
Options- A. the register's serial input is the counter input and the serial output is the counter output
- B. the parallel inputs provide the input signal and the output signal is taken from the serial data output
- C. serial in/serial out register must be used
- D. the serial output of the register is connected back to the serial input of the register Discuss
Counters problems
Search Results
Correct Answer: strobing
Correct Answer: stop counting
Correct Answer: ripple
Correct Answer: the clock signal
Correct Answer: level management
Correct Answer: feedback
Correct Answer: 1.25 kHz
Correct Answer: four-bit asynchronous binary counter
Correct Answer: decade
Correct Answer: the serial output of the register is connected back to the serial input of the register
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
