Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Combinational Logic Circuits See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The K-map in the figure below shows the correct implementation of the expression X = ACD + AB(CD + BC).
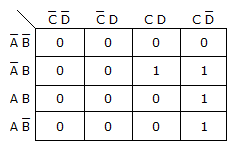
Options- A. True
- B. False
- Correct Answer
- False
- 1. A byte has 8 bits.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. A popular waveform generator is the Johnson shift counter.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. An ADC is an analog-to-digital converter.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. An inverter performs a NOT operation.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. Antifuse devices are volatile.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 6. Address multiplexing is used to reduce the number of address lines.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. Which type of ROM has to be custom built by the factory?
Options- A. ROM
- B. mask ROM
- C. EPROM
- D. EEPROM Discuss
- 8. The RST pin requires a HIGH to reset the 8051 microcontroller.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. How many clock pulses will be required to completely load serially a 5-bit shift register?
Options- A. 2
- B. 3
- C. 4
- D. 5 Discuss
- 10. A data selector is also called a demultiplexer.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: mask ROM
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 5
Correct Answer: False
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
