Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Memory and Storage See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The basic purpose of tristate or open-collector outputs on a memory is to ________.
Options- A. isolate devices connected to a common bus
- B. simplify the circuitry
- C. provide faster transitions of the output
- D. increase the output current
- Correct Answer
- isolate devices connected to a common bus
- 1. The content of a simple programmable logic device (PLD) consists of:
Options- A. fuse-link arrays
- B. thousands of basic logic gates
- C. advanced sequential logic functions
- D. thousands of basic logic gates and advanced sequential logic functions Discuss
- 2. A counter has a specified sequence of states, but a shift register does not.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. ROMs are used to store data on a permanent basis.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. A microprocessor with the necessary support circuits will include at least two memory ICs: ROM or EPROM, and a RAM.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. What is the acquisition time of the AD1154 sample-and-hold IC?
Options- A. 1.5 µs
- B. 2.5 µs
- C. 3.5 µs
- D. 4.5 µs Discuss
- 6. Which of the figures shown below represents the exclusive-NOR gate?
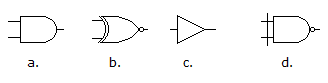
Options- A. a
- B. b
- C. c
- D. d Discuss
- 7. The device that places its input data onto one of several outputs is a ________.
Options- A. demultiplexer
- B. multiplexer
- C. comparator
- D. counter Discuss
- 8. Digital computers use an easier method to subtract binary numbers, called one's complement.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. With interrupt-driven I/O, if two or more devices request service at the same time, ________.
Options- A. the device closest to the CPU gets priority
- B. the device that is fastest gets priority
- C. the device assigned the highest priority is serviced first
- D. the system is likely to crash Discuss
- 10. Asynchronous counters are often called ________ counters.
Options- A. toggle
- B. ripple
- C. binary
- D. flip-flop Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: thousands of basic logic gates and advanced sequential logic functions
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 3.5 µs
Correct Answer: b
Correct Answer: demultiplexer
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: the device assigned the highest priority is serviced first
Correct Answer: ripple
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
