Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Memory and Storage See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
In DRAM operations, it is assumed that R/W is in its ________ state during a ________ operation.
Options- A. HIGH, read
- B. Hi-Z, write
- C. HIGH, write
- D. Hi-Z, read
- Correct Answer
- HIGH, read
- 1. What type of logic circuit is shown below and what logic function is being performed?

Options- A. It is an NMOS AND gate.
- B. It is a CMOS AND gate.
- C. It is a CMOS NOR gate.
- D. It is a PMOS NAND gate. Discuss
- 2. An inverter output is the complement of its input.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. A half-adder does not have ________.
Options- A. carry in
- B. carry out
- C. two inputs
- D. all of the above Discuss
- 4. The AD7524, a CMOS IC available from several IC manufacturers, is an eight-bit D/A converter that uses a(n) ________.
Options- A. sample-and-hold circuit
- B. R/2R ladder network
- C. multiplexer
- D. 10 µs clock Discuss
- 5. A binary number can be converted to be viewed on a 7-segment display by a(n) ________.
Options- A. decoder
- B. encoder
- C. multiplexer
- D. magnitude comparator Discuss
- 6. Convert the following octal number to decimal.
178
Options- A. 51
- B. 82
- C. 57
- D. 15 Discuss
- 7. The final step in the device programming sequence is ________.
Options- A. compiling
- B. downloading
- C. simulation
- D. synthesis Discuss
- 8. Polled I/O works best when ________.
Options- A. there are no priority considerations
- B. priority considerations are frequent
- C. the polling rate exceeds 1000 s
- D. the polling rate is below 1000 s Discuss
- 9. What function is performed by the block labeled X in the given figure?
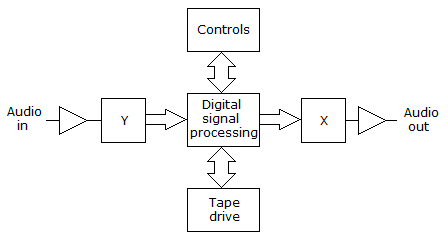
Options- A. Analog-to-digital conversion
- B. Digital-to-analog conversion
- C. Audio ON/OFF control
- D. Power supply for the audio amplifier Discuss
- 10. The GAL22V10 has 12 outputs pins and 10 input pins.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: It is a CMOS NOR gate.
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: carry in
Correct Answer: R/2R ladder network
Correct Answer: decoder
Correct Answer: 15
Correct Answer: downloading
Correct Answer: there are no priority considerations
Correct Answer: Digital-to-analog conversion
Correct Answer: False
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
