Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Computer Hardware and Software See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
To keep the number of IC pins to a minimum, the 8085 uses a multiplexed bus.
Options- A. True
- B. False
- Correct Answer
- True
- 1. After the first time constant, a transient current has changed by _______________ %, leaving _______________ % remaining.
Options- A. 63.2, 36.8
- B. 36.8, 63.2
- C. 13.5, 86.5
- D. 86.5, 13.5 Discuss
- 2. A measure of the repeatability of a measurement of some quantity is
Options- A. error
- B. precision
- C. accuracy
- D. significant Discuss
- 3. When an input signal reduces the channel size, the process is called:
Options- A. enhancement
- B. substrate connecting
- C. gate charge
- D. depletion Discuss
- 4.
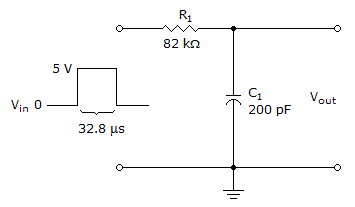
What voltage will the capacitor charge up to in the given circuit for the single input pulse shown?
Options- A. 3.15 V
- B. 4.3 V
- C. 4.75 V
- D. 4.9 V Discuss
- 5. Transistors are controlled to operate as a switch or to operate as a variable resistor.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 6. The voltmeter will read 18 volts.
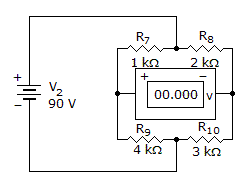
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. When does maximum power transfer happen from the source to the load?
Options- A. When the source resistance is greater than the load resistance
- B. When the source resistance is less than the load resistance
- C. When there is negligible source resistance
- D. When the source resistance equals the load resistance Discuss
- 8. What is the impedance of a series RC circuit that consists of a 0.22 µF capacitor and a 200-ohm resistor connected to a 3 kHz source?
Options- A. 214 ohms
- B. 313 ohms
- C. 414 ohms
- D. 880 ohms Discuss
- 9. What is the frequency of this 555 astable multivibrator?
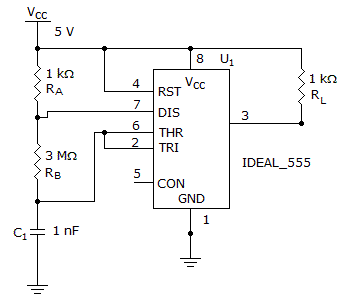
Options- A. 278 Hz
- B. 178 Hz
- C. 78 Hz
- D. 8 Hz Discuss
- 10. An 8 V power source is charging a capacitor. How many volts will be across the capacitor at the second time constant?
Options- A. 1 volt
- B. 3 volts
- C. 5 volts
- D. 7 volts Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 63.2, 36.8
Correct Answer: precision
Correct Answer: depletion
Correct Answer: 4.3 V
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: When the source resistance equals the load resistance
Correct Answer: 313 ohms
Correct Answer: 178 Hz
Correct Answer: 7 volts
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
