Discussion
Home ‣ C Programming ‣ Pointers See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
What will be the output of the program?
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int i=3, *j, k; j = &i; printf("%d\n", i**j*i+*j); return 0; }
Options- A. 30
- B. 27
- C. 9
- D. 3
- Correct Answer
- 30
- 1. Point out the error in the program?
typedef struct data mystruct; struct data { int x; mystruct *b; };
Options- A. Error: in structure declaration
- B. Linker Error
- C. No Error
- D. None of above Discuss
- 2. Left shifting an unsigned int or char by 1 is always equivalent to multiplying it by 2.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. Can you combine the following two statements into one?
char *p; p = (char*) malloc(100);
Options- A. char p = *malloc(100);
- B. char *p = (char) malloc(100);
- C. char *p = (char*)malloc(100);
- D. char *p = (char *)(malloc*)(100); Discuss
- 4. How many bytes are occupied by near, far and huge pointers (DOS)?
Options- A. near=2 far=4 huge=4
- B. near=4 far=8 huge=8
- C. near=2 far=4 huge=8
- D. near=4 far=4 huge=8 Discuss
- 5. Can a structure can point to itself?
Options- A. Yes
- B. No Discuss
- 6. What will be the output of the program if the array begins 1200 in memory?
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int arr[]={2, 3, 4, 1, 6}; printf("%u, %u, %u\n", arr, &arr[0], &arr); return 0; }
Options- A. 1200, 1202, 1204
- B. 1200, 1200, 1200
- C. 1200, 1204, 1208
- D. 1200, 1202, 1200 Discuss
- 7. What will be the output of the program?
#include<stdio.h> int main() { union a { int i; char ch[2]; }; union a u; u.ch[0]=3; u.ch[1]=2; printf("%d, %d, %d\n", u.ch[0], u.ch[1], u.i); return 0; }
Options- A. 3, 2, 515
- B. 515, 2, 3
- C. 3, 2, 5
- D. 515, 515, 4 Discuss
- 8. What will be the output of the program given below in 16-bit platform?
#include<stdio.h> int main() { enum value{VAL1=0, VAL2, VAL3, VAL4, VAL5} var; printf("%d\n", sizeof(var)); return 0; }
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 4
- D. 10 Discuss
- 9. What will be the output of the program?
#include<stdio.h> int main() { struct byte { int one:1; }; struct byte var = {1}; printf("%d\n", var.one); return 0; }
Options- A. 1
- B. -1
- C. 0
- D. Error Discuss
- 10. Point out the error in the program?
#include<stdio.h> int main() { struct bits { float f:2; }bit; printf("%d\n", sizeof(bit)); return 0; }
Options- A. 4
- B. 2
- C. Error: cannot set bit field for float
- D. Error: Invalid member access in structure Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: No Error
Explanation:
Here the type name
mystruct is known at the point of declaring the structure, as it is already defined.
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: char *p = (char*)malloc(100);
Correct Answer: near=2 far=4 huge=4
Explanation:
near=2,
far=4 and
huge=4 pointers exist only under DOS. Under windows and Linux every pointers is 4 bytes long.
Correct Answer: Yes
Explanation:
A structure pointing to itself is called self-referential structures.
Correct Answer: 1200, 1200, 1200
Explanation:
Step 1: int arr[]={2, 3, 4, 1, 6}; The variable arr is declared as an integer array and initialized.
Step 2: printf("%u, %u, %u\n", arr, &arr[0], &arr); Here,
The base address of the array is 1200.
=> arr, &arr is pointing to the base address of the array arr.
=> &arr[0] is pointing to the address of the first element array arr. (ie. base address)
Hence the output of the program is 1200, 1200, 1200
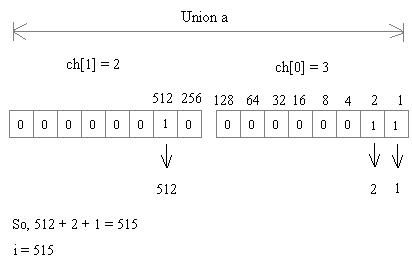
Correct Answer: 3, 2, 515
Explanation:
The system will allocate 2 bytes for the union.
The statements u.ch[0]=3; u.ch[1]=2; store data in memory as given below.
Correct Answer: 2
Correct Answer: -1
Correct Answer: Error: cannot set bit field for float
Comments
There are no comments.More in C Programming:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
