Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Microprocessor Fundamentals See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
When referring to instruction words, a mnemonic is:
Options- A. a short abbreviation for the operand address
- B. a short abbreviation for the operation to be performed
- C. a short abbreviation for the data word stored at the operand address
- D. shorthand for machine language
- Correct Answer
- a short abbreviation for the operation to be performed
- 1. Why must CMOS devices be handled with care?
Options- A. so they don't get dirty
- B. because they break easily
- C. because they can be damaged by static electricity discharge Discuss
- 2. What decimal value is required to produce an output at "X"?
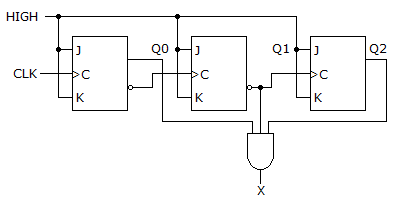
Options- A. 1
- B. 1 or 4
- C. 2
- D. 5 Discuss
- 3. Which is not a part of a GAL16V8's OLMC?
Options- A. TSMUX
- B. OMUX
- C. FMUX
- D. PSMUX Discuss
- 4. Output will be a LOW for any case when one or more inputs are zero for a(n):
Options- A. OR gate
- B. NOT gate
- C. AND gate
- D. NOR gate Discuss
- 5. The sum of 11101 + 10111 equals ________.
Options- A. 110011
- B. 100001
- C. 110100
- D. 100100 Discuss
- 6. Hex is often used in digital applications as a shorthand way to represent strings of bits.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. Four cascaded modulus-10 counters have an overall modulus of ________.
Options- A. 10
- B. 100
- C. 1,000
- D. 10,000 Discuss
- 8. VHDL is not a new language.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. Which is not a removable drive?
Options- A. Zip
- B. Jaz
- C. Hard
- D. SuperDisk Discuss
- 10. Which microprocessor has multiplexed data and address lines?
Options- A. 8086/8088
- B. 80286
- C. 80386
- D. Pentium Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: because they can be damaged by static electricity discharge
Correct Answer: 5
Correct Answer: PSMUX
Correct Answer: AND gate
Correct Answer: 110100
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 10,000
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: Hard
Correct Answer: 8086/8088
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
