Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Digital Signal Processing See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
If a DAC has a full-scale, or maximum, output of 12 V and accuracy of
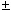 0.1%, then the maximum error for any output voltage is ________.
0.1%, then the maximum error for any output voltage is ________.
Options- A. 12 V
- B. 120 mV
- C. 12 mV
- D. 0 V
- Correct Answer
- 12 mV
- 1. In Boolean algebra, the word "literal" means ________.
Options- A. a product term
- B. all the variables in a Boolean expression
- C. the inverse function
- D. a variable or its complement Discuss
- 2. Which of the statements below best describes the basic operation of a dual-slope A/D converter?
Options- A. The input voltage is used to set the frequency of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The VCO quits changing frequency when the input voltage stabilizes. The frequency of the VCO, which is proportional to the analog input voltage, is measured and is displayed on the digital display as a voltage reading.
- B. A ramp generator is used to enable a counter through a comparator. When the ramp voltage equals the input voltage, the counter is latched and then reset. The counter reading is proportional to the input voltage since the ramp is changing at a constant V/second rate.
- C. A ramp voltage and analog input voltage are applied to a comparator. As the input voltage causes the integrating capacitor to charge, it will at some point equal the ramp voltage. The ramp voltage is measured and displayed on the digital panel meter.
- D. Two ramps are generated: one by the input voltage and the other by a reference voltage. The input voltage ramp charges the integrating capacitor, while the reference voltage discharges the capacitor and enables the counter until the capacitor is discharged, at which time the counter value is loaded into the output latches. Discuss
- 3. One application of a digital multiplexer is to facilitate:
Options- A. data generation
- B. serial-to-parallel conversion
- C. parity checking
- D. data selector Discuss
- 4. The action of ________ a FF or latch is also called resetting.
Options- A. breaking
- B. clearing
- C. freeing
- D. changing Discuss
- 5. A flip-flop operation is described as a toggle when the result after a clock is ________.
Options- A.

- B.

- C.
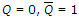
- D.
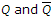 change to opposite states
Discuss
change to opposite states
Discuss
- 6. Synchronous (parallel) counters eliminate the delay problems encountered with asynchronous (ripple) counters because the:
Options- A. input clock pulses are applied only to the first and last stages.
- B. input clock pulses are applied only to the last stage.
- C. input clock pulses are applied simultaneously to each stage.
- D. input clock pulses are not used to activate any of the counter stages. Discuss
- 7. In the frequency counter, a pulse shaper block is needed to ensure that the unknown signal, whose frequency is to be measured, will be compatible with the clock input for the counter block.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. When the output of the NOR gate S-R flip-flop is in the HOLD state (no change), the inputs are ________.
Options- A. S = 1, R = 1
- B. S = 1, R = 0
- C. S = 0, R = 1
- D. S = 0, R = 0 Discuss
- 9. The primary disadvantage of the simultaneous A/D converter is ________.
Options- A. that it requires the input voltage to be applied to the inputs simultaneously
- B. the long conversion time required
- C. the large number of output lines required to simultaneously decode the input voltage
- D. the large number of comparators required to represent a reasonable-sized binary number Discuss
- 10. An offset error in a DAC will show up as an incorrect analog output ________.
Options- A. only for higher value inputs
- B. only for lower value inputs
- C. only for certain (scattered) inputs
- D. for all inputs Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: a variable or its complement
Correct Answer: Two ramps are generated: one by the input voltage and the other by a reference voltage. The input voltage ramp charges the integrating capacitor, while the reference voltage discharges the capacitor and enables the counter until the capacitor is discharged, at which time the counter value is loaded into the output latches.
Correct Answer: data selector
Correct Answer: clearing
Correct Answer:
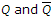 change to opposite states
change to opposite states Correct Answer: input clock pulses are applied simultaneously to each stage.
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: S = 0, R = 0
Correct Answer: the large number of comparators required to represent a reasonable-sized binary number
Correct Answer: for all inputs
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
