Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Flip-Flops See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Which of the following is correct for a D latch?
Options- A. The output toggles if one of the inputs is held HIGH.
- B. Q output follows the input D when the enable is HIGH.
- C. Only one of the inputs can be HIGH at a time.
- D. The output complement follows the input when enabled.
- Correct Answer
- Q output follows the input D when the enable is HIGH.
- 1. Which is the decimal number for the BCD number, 10110110?
Options- A. 182
- B. 36
- C. 116
- D. 10110110 is not a valid BCD number. Discuss
- 2. Solve this BCD problem: 0101 + 0110 = ________.
Options- A. 00010111BCD
- B. 00001001BCD
- C. 00010001BCD
- D. 00010011BCD Discuss
- 3. The items that you can physically touch in a computer system are called:
Options- A. software
- B. firmware
- C. hardware
- D. none of the above Discuss
- 4. In the digital clock project, the 60 Hz signal is sent through a Schmitt-trigger circuit to produce sine wave pulses at the rate of 60 pps.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. Power-supply decoupling uses a radio-frequency capacitor to short out high frequency spikes.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 6. The device shown here is most likely a ________.
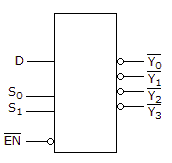
Options- A. comparator
- B. multiplexer
- C. demultiplexer
- D. parity generator Discuss
- 7. The distinction between CPLDs and FPGAs is ________.
Options- A. well known
- B. very small
- C. often fuzzy
- D. very large Discuss
- 8. The advantage of a J-K flip-flop over an S-R FF is that ________.
Options- A. it has fewer gates
- B. it has only one output
- C. it has no invalid states
- D. it does not require a clock input Discuss
- 9. Bidirectional shift registers can shift data either right or left.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. Main computer memory is usually DRAM because of its high density and low cost; cache memory is usually SRAM because of its high speed.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 10110110 is not a valid BCD number.
Correct Answer: 00010001BCD
Correct Answer: hardware
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: demultiplexer
Correct Answer: often fuzzy
Correct Answer: it has no invalid states
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
