Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Flip-Flops See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
What does the triangle on the clock input of a J-K flip-flop mean?
Options- A. level enabled
- B. edge-triggered
- Correct Answer
- edge-triggered
- 1. Adding an odd-parity bit to ASCII hex code 2B results in 10101011.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. A half-adder circuit would normally be used each time a carry input is required in an adder circuit.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. A CD-ROM is a form of read-only memory in which data are stored as ________.
Options- A. magnetic "bubbles"
- B. magnetized spots
- C. "pits" on an optical disk
- D. tiny "pinholes" in an opaque substance Discuss
- 4. On the fifth clock pulse, a 4-bit Johnson sequence is Q0 = 0, Q1 = 1, Q2 = 1, and Q3 = 1. On the sixth clock pulse, the sequence is ________.
Options- A. Q0 = 1, Q1 = 0, Q2 = 0, Q3 = 0
- B. Q0 = 1, Q1 = 1, Q2 = 1, Q3 = 0
- C. Q0 = 0, Q1 = 0, Q2 = 1, Q3 = 1
- D. Q0 = 0, Q1 = 0, Q2 = 0, Q3 = 1 Discuss
- 5. What is the difference between the 54XX and 74XX series of TTL logic gates?
Options- A. 54XX is faster.
- B. 54XX is slower.
- C. 54XX has a wider power supply and expanded temperature range.
- D. 54XX has a narrower power supply and contracted temperature range. Discuss
- 6. Synchronous construction reduces the delay time of a counter to the delay of:
Options- A. all flip-flops and gates
- B. all flip-flops and gates after a 3 count
- C. a single gate
- D. a single flip-flop and a gate Discuss
- 7. After each circuit in a subsection of a VHDL program has been ________, they can be combined and the subsection can be tested.
Options- A. designed
- B. tested
- C. engineered
- D. produced Discuss
- 8. CLB is the acronym for ________.
Options- A. Configurable Logic Block
- B. Configurable Logic Buffer
- C. Critical Logic Buffer
- D. Constant Logic Buffer Discuss
- 9. The given figure is most likely a ________.
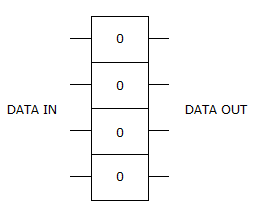
Options- A. register
- B. decoder
- C. counter
- D. multiplexer Discuss
- 10. For a three-input AND gate, with the input waveforms as shown below, which output waveform is correct?
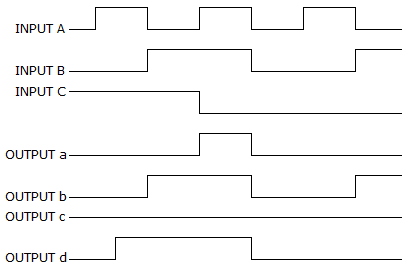
Options- A. a
- B. b
- C. c
- D. d Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: "pits" on an optical disk
Correct Answer: Q0 = 0, Q1 = 0, Q2 = 1, Q3 = 1
Correct Answer: 54XX has a wider power supply and expanded temperature range.
Correct Answer: a single flip-flop and a gate
Correct Answer: tested
Correct Answer: Configurable Logic Block
Correct Answer: register
Correct Answer: c
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
