Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Interfacing to the Analog World See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
What is the output voltage for the circuit shown below?
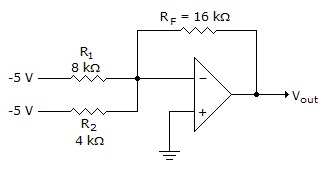
Options- A. 10 V
- B. 20 V
- C. 30 V
- D. 40 V
- Correct Answer
- 30 V
- 1. All I/O pins in the MAX7000S family have a tristate buffer.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. When the 2's-complement system is used, the number to be subtracted is changed to its 2's complement and then added to the minuend.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. In a BCD-to-seven-segment converter, why must a code converter be utilized?
Options- A. to convert the 4-bit BCD into 7-bit code
- B. to convert the 4-bit BCD into 10-bit code
- C. to convert the 4-bit BCD into Gray code
- D. No conversion is necessary. Discuss
- 4. When decimal numbers with several digits are to be added together using BCD adders ________.
Options- A. a separated BCD adder is required for each digit position
- B. the BCD adders must have the carry-outs grounded
- C. the BCD's must be grouped in twos
- D. full adders are also used Discuss
- 5. In the digital clock project, a MOD-60 BCD counter is made from a MOD-10 counter cascaded to a MOD-6 BCD counter.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 6. The inputs of a full adder are labeled A1, B1, and Cin.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. In HDL, a process is usually thought of as a wire connecting two points in a circuit.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. Binary numbers can be added together in a basic parallel-adder circuit when ________.
Options- A. negative numbers are in 2's-complement form
- B. negative numbers are in 1's-complement form
- C. all carry pins are grounded
- D. all negative numbers are noted Discuss
- 9. The binary subtraction 1 ? 1 = ________.
Options- A. difference = 0
borrow = 0 - B. difference = 1
borrow = 0 - C. difference = 1
borrow = 1 - D. difference = 0
borrow = 1
Discuss
- 10. The programming technologies that are used in CPLD devices are all nonvolatile.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: to convert the 4-bit BCD into 7-bit code
Correct Answer: a separated BCD adder is required for each digit position
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: negative numbers are in 2's-complement form
Correct Answer: difference = 0
borrow = 0
Correct Answer: True
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
