Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Memory and Storage See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
How many storage locations are available when a memory device has 12 address lines?
Options- A. 144
- B. 512
- C. 2048
- D. 4096
- Correct Answer
- 4096
- 1. The first microprocessor had a(n)________.
Options- A. 1-bit data bus
- B. 2-bit data bus
- C. 4-bit data bus
- D. 8-bit data bus Discuss
- 2. If a 3-input OR gate has eight input possibilities, how many of those possibilities will result in a HIGH output?
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 7
- D. 8 Discuss
- 3. The select inputs to a multiplexer may also be called address lines.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. How many 2-input NOR gates does it take to produce a 2-input NAND gate?
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 5. The 7476 and 74LS76 are both dual flip-flops.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 6. How many different states does a 3-bit asynchronous counter have?
Options- A. 2
- B. 4
- C. 8
- D. 16 Discuss
- 7. The invalid range for an input to TTL logic is from ________.
Options- A. 0 to 0.8 V
- B. 1.2 to 1.6 V
- C. 0.8 to 2.0 V
- D. 2.0 to 5.0 V Discuss
- 8. A typical fan-out for most TTL is 9.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. The outputs of the 74138 octal decoder are enabled when the enable inputs are
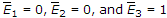 .
.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. Convert the following hexadecimal number to decimal.
B516
Options- A. 212
- B. 197
- C. 165
- D. 181 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 4-bit data bus
Correct Answer: 7
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 4
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 8
Correct Answer: 0.8 to 2.0 V
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 181
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
