Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Memory and Storage See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A CD-R disk is created by applying heat to special chemicals on the disk and these chemicals reflect less light than the areas that are not burned, thus creating the same effect as a pit does on a regular CD.
Options- A. True
- B. False
- Correct Answer
- True
- 1. The concurrent section of the hardware description is where the ________ are interconnected.
Options- A. functions
- B. components
- C. circuits
- D. macrofunctions Discuss
- 2. Output 6 of a 74138 octal decoder is selected when it is enabled by a data input of:
A0 = 1
A1 = 1
A2 = 0
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. Assume a ROM to be tested is compared with a known good ROM. If the checksums differ, the ROM is ________.
Options- A. very likely to be good
- B. definitely good
- C. very likely to be bad
- D. definitely bad Discuss
- 4. The most common TTL series ICs are:
Options- A. E-MOSFET
- B. 7400
- C. quad
- D. AC00 Discuss
- 5. Microcontrollers often have:
Options- A. CPUs
- B. RAM
- C. ROM
- D. all of the above Discuss
- 6. Before an SOP implementation, the expression
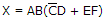 would require a total of how many gates?
would require a total of how many gates?
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 4
- D. 5 Discuss
- 7. The outputs of a 7485 four-bit magnitude comparator when the inputs are A = 0110 and B = 1010 are:
A < B is 1
A = B is 0
A > B is 1
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. How many outputs are on a BCD decoder?
Options- A. 4
- B. 16
- C. 8
- D. 10 Discuss
- 9. The GAL16V8 has eight dedicated input pins.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. The Boolean expression AB + CD is an example of ________.
Options- A. PAL
- B. GAL
- C. SOP
- D. POS Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: components
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: definitely bad
Correct Answer: 7400
Correct Answer: all of the above
Correct Answer: 5
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: 10
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: SOP
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
