Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Memory and Storage See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A 64-bit word consists of ________.
Options- A. 4 bytes
- B. 8 bytes
- C. 10 bytes
- D. 12 bytes
- Correct Answer
- 8 bytes
- 1. In the digital clock project, the ENT input and RCO output can be used for synchronous counter cascading.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. A pull-up resistor is a resistor used to keep a given point in a circuit HIGH when in the active state.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. The 74139 dual four-line demultiplexer functions as a demultiplexer if data input is on the
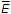 line.
line.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. When VGS = 0 on an N-channel MOSFET switch, there is no ________ between the source and the drain.
Options- A. voltage drop
- B. conductive channel
- C. capacitance
- D. inductance Discuss
- 5. The minimum number of flip-flops that can be used to construct a modulus-5 counter is ________.
Options- A. 3
- B. 5
- C. 8
- D. 10 Discuss
- 6. The timing network that sets the output frequency of a 555 astable circuit contains ________.
Options- A. three external resistors are used
- B. two external resistors and an external capacitor are used
- C. an external resistor and two external capacitors are used
- D. no external resistor or capacitor is required Discuss
- 7. When analog inputs from several sources are to be converted, a multiplexing technique can be used so that one ADC may be time-shared.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. A parallel in/serial out shift register enters all data bits simultaneously and transfers them out one bit at a time.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. In VHDL, if we need to remember a value it must be stored in a ________.
Options- A. function
- B. type declaration
- C. variable
- D. process Discuss
- 10. The summing outputs of a half- or full-adder are designated by which Greek symbol?
Options- A. omega
- B. theta
- C. lambda
- D. sigma Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: conductive channel
Correct Answer: 3
Correct Answer: two external resistors and an external capacitor are used
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: function
Correct Answer: sigma
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
