Discussion
Home ‣ Digital Electronics ‣ Digital Arithmetic Operations and Circuits See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
One way to make a four-bit adder perform subtraction is by:
Options- A. inverting the output.
- B. inverting the carry-in.
- C. inverting the B inputs.
- D. grounding the B inputs.
- Correct Answer
- inverting the B inputs.
- 1. What distinguishes the look-ahead-carry adder?
Options- A. It is slower than the ripple-carry adder.
- B. It is easier to implement logically than a full adder.
- C. It is faster than a ripple-carry adder.
- D. It requires advance knowledge of the final answer. Discuss
- 2. CMOS stands for "complementary metal-oxide semiconductors" and the FETs are normally enhancement mode devices.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. An astable multivibrator is sometimes referred to as a clock.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. When the output of the NOR gate S-R flip-flop is Q = 0 and
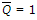 , the inputs are:
, the inputs are:
Options- A. S = 1, R = 1
- B. S = 1, R = 0
- C. S = 0, R = 1
- D. S = 0, R = 0 Discuss
- 5. What is the maximum time required before a dynamic RAM must be refreshed?
Options- A. 2 ms
- B. 4 ms
- C. 8 ms
- D. 10 ms Discuss
- 6. For a three-input NOR gate, with the input waveforms as shown below, which output waveform is correct?
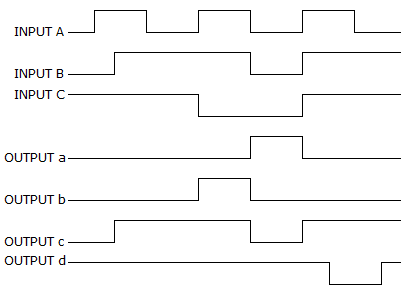
Options- A. a
- B. b
- C. c
- D. d Discuss
- 7. The noise immunity of a logic circuit refers to the circuit's ability to tolerate noise by causing spurious charges in the output voltage.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. The main advantage of bipolar (TTL) memories over MOS memories is speed.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. A very critical dimension in project management is ________.
Options- A. cost
- B. skill
- C. time
- D. personnel Discuss
- 10. A counter-ramp ADC stops counting when ________.
Options- A. the input voltage equals the DAC staircase voltage
- B. the counter reaches a maximum count
- C. the input voltage equals 5 volts
- D. the DAC staircase voltage equals 5 volts Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: It is faster than a ripple-carry adder.
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: S = 0, R = 1
Correct Answer: 2 ms
Correct Answer: a
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: time
Correct Answer: the input voltage equals the DAC staircase voltage
Comments
There are no comments.More in Digital Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
