Irrigation problems
- 1. The sensitivity of a rigid module, is
Options- A. 2.00
- B. 1.50
- C. 1.00
- D. 0.50
- E. zero Discuss
Correct Answer: zero
- 2. A hydraulic jump is generally formed when a stream moving with
Options- A. a hyper-critical velocity meets a stream moving with a critical velocity
- B. a hyper-critical velocity meets a stream moving with a hyper-critical velocity
- C. A hyper-critical velocity meets a stream moving with a sub-critical velocity
- D. a sub-critical velocity meets a stream moving with a hyper-critical velocity. Discuss
Correct Answer: A hyper-critical velocity meets a stream moving with a sub-critical velocity
- 3. Meandering of a river generally occurs, in
Options- A. rocky stage
- B. delta stage
- C. boulder stage
- D. trough stage. Discuss
Correct Answer: trough stage.
- 4. Regime conditions in a channel may occur if
Options- A. discharge is constant
- B. channel flows uniformly in incoherent alluvium as that transported in suspension
- C. silt grade and silt charge are constant
- D. all the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: all the above.
- 5. The main cause of silting up a channel,
Options- A. non-regime section
- B. inadequate slope
- C. defective head regulator
- D. defective outlets
- E. all the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: all the above.
- 6. The optimum depth of kor watering for a rice crop, is
Options- A. 23.0 cm
- B. 19.0 cm
- C. 17.5 cm
- D. 13.5 cm
- E. 12.0 cm Discuss
Correct Answer: 19.0 cm
- 7. Bligh's theory of seepage assumes
Options- A. equal weightage to the horizontal and vertical creep
- B. more weightage to horizontal creep than vertical creep
- C. less weightage to horizontal creep than vertical creep
- D. loss of head follows the sine curve. Discuss
Correct Answer: equal weightage to the horizontal and vertical creep
- 8. In north Indian Plains, optimum depth of kor watering for wheat, is
Options- A. 23.0 cm
- B. 19.0 cm
- C. 17.5 cm
- D. 13.5 cm
- E. 12.0 cm Discuss
Correct Answer: 13.5 cm
- 9. If ? is the depth of water in metres, B is the number of days of base period and D is the duty in hactare/cumec, the relationship which holds good, is
Options- A.
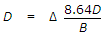
- B.
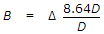
- C.
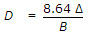
- D.
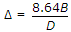
- E. none of these. Discuss
Correct Answer:
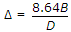
- 10. Canals taken off from ice-fed perennial rivers, are known
Options- A. permanent canals
- B. ridge canals
- C. perennial canals
- D. inundation canals
- E. ice canals. Discuss
Correct Answer: perennial canals
More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
