Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Magnetism and Electromagnetism See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The ___ is an electromagnetic device that contains a coil rotating on a jeweled bearing mount.
Options- A. permanent-magnet speaker
- B. d'Arsonval movement
- C. single-pole, double-throw relay
- D. crankshaft position sensor
- Correct Answer
- d'Arsonval movement
- 1. A differentiator circuit can be used to convert a pulse input to a nearly constant dc output.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2.
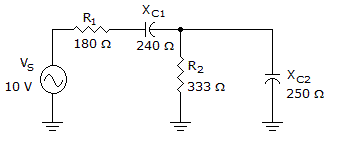
What is the phase angle in the given circuit?
Options- A. 14.95°
- B. 36.88°
- C. 0°
- D. 90° Discuss
- 3. If a charged capacitor is disconnected from a circuit, it will:
Options- A. immediately discharge
- B. recharge
- C. remain charged
- D. leak the charge Discuss
- 4. A capacitor's rate of charge is considered:
Options- A. magnetic
- B. a current block
- C. linear
- D. exponential Discuss
- 5. Faraday's law states that the polarity of induced voltage in a coil is in opposition to the current change through that coil.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 6.

The phase angle in the circuit in the given circuit is approximately equal to ______.
Options- A. 53°
- B. 90°
- C. 37°
- D. 0° Discuss
- 7. If the reactive power of a circuit is 50 mW while the apparent power is 64 mW, then what is the true power of the circuit?
Options- A. 14 mW
- B. 36 mW
- C. 40 mW
- D. 114 mW Discuss
- 8.
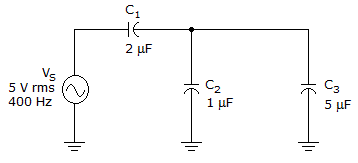
The total circuit reactance is ______ in the given circuit.
Options- A. 50 Ω
- B. 140 Ω
- C. 265 Ω
- D. 676 Ω Discuss
- 9. An asynchronous decade counter increases its value by ten for each clock pulse.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. It takes two memory locations (16 bits each) to store an address in the 8085 system.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: 14.95°
Correct Answer: leak the charge
Correct Answer: exponential
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: 37°
Correct Answer: 40 mW
Correct Answer: 265 Ω
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: False
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
