Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Sequential Logic Circuits See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
In order to use a shift register as a counter, ________.
Options- A. the register's serial input is the counter input and the serial output is the counter output
- B. the parallel inputs provide the input signal and the output signal is taken from the serial data output
- C. a serial-in, serial-out register must be used
- D. the serial output of the register is connected back to the serial input of the register
- Correct Answer
- the serial output of the register is connected back to the serial input of the register
- 1. Logic gate circuits contain predictable gate functions that open their outputs.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. A reverse biased diode will act as an open switch.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. A transducer does not convert energy from one form to another.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. What is the standard TTL noise margin?
Options- A. 5.0 V
- B. 0.2 V
- C. 0.8 V
- D. 0.4 V Discuss
- 5. The total resistance of a series circuit always depends on the highest value resistor in that circuit.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 6. A transistor used in a digital circuit will have two operating states, which are cutoff and saturation.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. What is the output voltage?
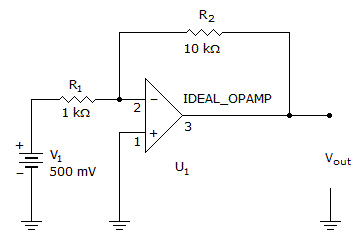
Options- A. 15 V
- B. 5 V
- C. ?5 V
- D. ?15 V Discuss
- 8. A transistor may be used as a switching device or as a:
Options- A. fixed resistor
- B. tuning device
- C. rectifier
- D. variable resistor Discuss
- 9. The total resistance of a series circuit is equal to the average of all the resistance values.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. Ferromagnetic materials have pre-existing magnetic fields.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: 0.4 V
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: ?5 V
Correct Answer: variable resistor
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: False
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
