Discussion
Home ‣ Non Verbal Reasoning ‣ Image Analysis See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Find out how will the key figure (X) look like after rotation.
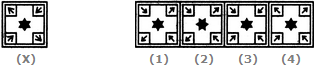
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4
- Correct Answer
- 2
- 1. Find the missing figure of the series from the given responses:

Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 2. Select a suitable figure from the answer figures that would replace the question mark (?) from question figure.
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 3. Two positions of a dice are shown below. When the heart shape is at the top, what will be at the bottom?
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 4. Select the one which is different from the other three responses
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 5.
When a mirror is placed on the line AB, then which right image of the given figure?

Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. none Discuss
- 6. What will come in place of?:

Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 7. Choose the figure which is different from the rest.
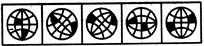 (1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4
- E. 5 Discuss
- 8. Choose a figure which would most closely resemble the unfolded form of Figure (3).
Options- A. (a)
- B. (b)
- C. (c)
- D. (d) Discuss
- 9. Choose the figure which is different from the rest.
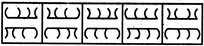 (1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4
- E. 5 Discuss
- 10. Find out the alternative figure which contains figure (X) as its part.
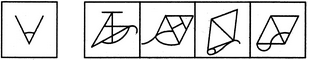 (X) (1) (2) (3) (4)
(X) (1) (2) (3) (4)
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 2
Explanation:
As per the given above question figures , we can see that
In each subsequent figure the design rotates through 90° clockwise and the oblique lines are rearranged.
Therefore , figure ( 2 ) will come on the place of ? in question figure .As shown in answer figures .
Correct Answer: 1
Explanation:
The element moves in the sequence.
Correct Answer: 4
Explanation:
On the basis of question figure pattern ,
Here the common faces with star are in same positions .
When the heart shape is at the top, the rhombus would be on the bottom.
Correct Answer: 4
Explanation:
As we can see that The fourth figure is different from the other three figures.So , figure ( 4 ) is correct answer .
Correct Answer: 2
Explanation:
Correct Answer: 2
Explanation:
On the basis of given figures in above question , we can see that
From first figure to third figure two smaller line segments are added. Similarly, two smaller line segments should be added to the second figure to get the Answer figure.
Hence , figure ( 2 ) will come on the place of ? in question figure .As shown in answer figures .
Correct Answer: 5
Explanation:
Correct Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Since cutting from the mid line , it will create a circle around the mid line.
Correct Answer: 5
Explanation:
Correct Answer: 4
Explanation:
Comments
There are no comments.Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
