Discussion
Home ‣ Non Verbal Reasoning ‣ Figure Matrix See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Select a suitable figure from the four alternatives that would complete the figure matrix.
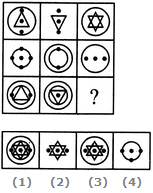
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4
- Correct Answer
- 2
ExplanationThe third figure in each row comprises of parts which are not common to the first two figures. - 1. NA
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 2. NA
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 3. NA
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 4. NA
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 5. NA
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 6. NA
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 7. NA
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 8. NAME
Options- A. .
- B. .
- C. .
- D. . Discuss
- 9. NA
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 10. NA
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 2
Explanation:
NA
Correct Answer: 4
Explanation:
NA
Correct Answer: 1
Explanation:
NA
Correct Answer: 3
Explanation:
NA
Correct Answer: 3
Explanation:
NA
Correct Answer: 1
Explanation:
NA
Correct Answer: 1
Explanation:
NA
Correct Answer: .
Explanation:
Answer B
Correct Answer: 4
Explanation:
NA
Correct Answer: 1
Explanation:
NA
Comments
There are no comments.Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
