Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Analog and Digital Converters See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The resolution of a 0?5 V 6-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) is:
Options- A. 63%
- B. 64%
- C. 1.56%
- D. 15.6%
- Correct Answer
- 1.56%
- 1. The silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) is a three-layer device consisting of a gate, an anode, and a cathode.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. The maximum potential a material can withstand without rupture is called breakdown voltage.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3.
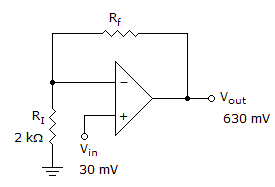
The feedback resistor has a value of ______ in the given circuit
Options- A. 2 kΩ
- B. 10.5 kΩ
- C. 21 kΩ
- D. 40 kΩ Discuss
- 4. If the drain, source, and channel of a MOSFET are all a p-type material, and it operates in both modes, this is an n-channel D-MOSFET.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. A 22-gauge wire will have a diameter in mils of:
Options- A. 10.03
- B. 22.35
- C. 45.26
- D. 71.96 Discuss
- 6. The electrical energy consumed by a coil is stored in the form of:
Options- A. an electrical field
- B. a force field
- C. an electrostatic field
- D. a magnetic field Discuss
- 7. How many basic types of resistors exist?
Options- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4 Discuss
- 8. In parallel RC circuits, the larger the value of C, the larger the phase angle.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. A zener diode can be used to provide voltage regulation in a power supply.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. An RL filter could be a high-pass or a low-pass filter.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: False
Explanation:
A silicon-controlled rectifier (or semiconductor-controlled rectifier) is a four-layer solid state device that controls current. The name "silicon controlled rectifier" or SCR is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The SCR was developed by a team of power engineers led by Gordon Hall and commercialized by Frank W. "Bill" Gutzwiller in 1957.
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: 40 kΩ
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: 22.35
Correct Answer: a magnetic field
Correct Answer: 2
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
