Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Resistance and Power See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
One ampere of current flowing through one ohm of resistance is equal to:
Options- A. 1 horsepower
- B. 1 Btu
- C. 1 watt
- D. 1 joule
- Correct Answer
- 1 watt
- 1. The opposition to ac by an inductor is directly proportional to ___.
Options- A. resistance
- B. reactance
- C. frequency
- D. voltage Discuss
- 2. An air-core inductor has a metal core.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3.
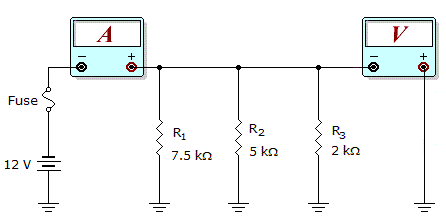
What would these meter readings indicate about the circuit in the given circuit?
Meter Readings: I = 10 mA, V = 12 V
Options- A. R1 is open.
- B. R2 is open.
- C. The fuse is open.
- D. The circuit is operating normally. Discuss
- 4.
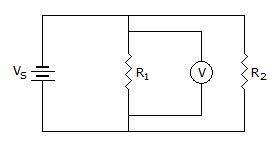
If the voltmeter indicates 12 V in the given circuit, the voltage across R2 equals ___.
Options- A. 12 V
- B. VS minus 12 V
- C. 0 V
- D. More information is needed to find the voltage across R2. Discuss
- 5. If a 220 Ω, a 100 Ω, and a 180 Ω resistor are connected in series across a 12 V source, the circuit current equals ___.
Options- A. 41.67 A
- B. 120 mA
- C. 500 A
- D. 24 mA Discuss
- 6.
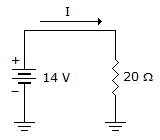
What is the power in the given circuit?
Options- A. 3.92 kW
- B. 280 W
- C. 28.6 W
- D. 9.8 W Discuss
- 7. Doubling the voltage across a resistor will cut the current by half.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. Common-mode signals have _____.
Options- A. the same amplitude
- B. the same phase
- C. the same frequency
- D. All of the above Discuss
- 9. If you borrow from a position that contains a 0, you must borrow from the more significant bit that contains a 1. All 0s up to that point become 1s, and the digit last borrowed from becomes a 0.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. Resistance is the same as impedance in an RC circuit.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: frequency
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: The circuit is operating normally.
Correct Answer: 12 V
Correct Answer: 24 mA
Correct Answer: 9.8 W
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: All of the above
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
