Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Special-Purpose Op-Amp Circuits See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
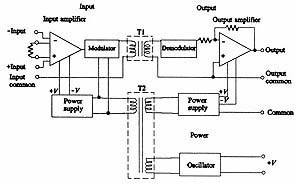
This circuit is a setup for
Options- A. an antilog amplifier
- B. a constant-current source
- C. an instrumentation amplifier
- D. an isolation amplifier
- Correct Answer
- an isolation amplifier
- 1. A transformer that has 700 turns in the primary and 35 turns in the secondary has a turns ratio of 20:1.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. The operands in an addition operation consist of the augend and the addend.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. In a BJT, the collector current is approximately equal to the base current.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. A sine wave has:
Options- A. four quadrants
- B. two alternations
- C. one period
- D. all of the above Discuss
- 5. The greater the selectivity, the wider the bandwidth.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 6. The unit of magnetic flux density is the weber.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. PROMs are volatile.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. A monostable multivibrator must be triggered.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. Generally, increasing the resistance in a circuit will decrease the current.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. A capacitor takes ___ time constants to charge to 95% of its capacity.
Options- A. 2
- B. 3
- C. 4
- D. 5 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: all of the above
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 3
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
