Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ RC Circuits See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
What is the effect of increasing the resistance in a series RC circuit?
Options- A. There will be no effect at all.
- B. The current will increase.
- C. The phase shift will decrease.
- D. The input voltage will increase.
- Correct Answer
- The phase shift will decrease.
- 1.
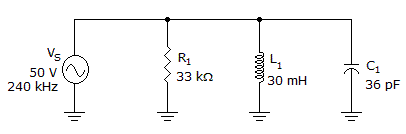
The phase angle is ______ in the given circuit.
Options- A. 34.5°
- B. 43.3°
- C. 46.7°
- D. 55.5° Discuss
- 2. In order for feedback oscillators to have any practical value, the gain has to be
Options- A. < 1
- B. self-adjusting
- C. stabilized
- D. nonlinear Discuss
- 3. If 5 V and 16 V power supplies are connected in series-opposing, what is the total voltage?
Options- A. 11 V
- B. 16 V
- C. 21 V
- D. 80 V Discuss
- 4. The number 560,000 is expressed in scientific notation.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. A 2% 55 kΩ resistor would have a color coding of green, green, black, red, red.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 6.

Which is a true statement about the circuit in the given circuit?
Options- A. The batteries are series-aiding and the total source voltage equals 21 V.
- B. The batteries are series-opposing and the total source voltage equals 3 V.
- C. The batteries are series-aiding and the total source voltage equals 3 V.
- D. The batteries are series-opposing and the total source voltage equals 21 V. Discuss
- 7.
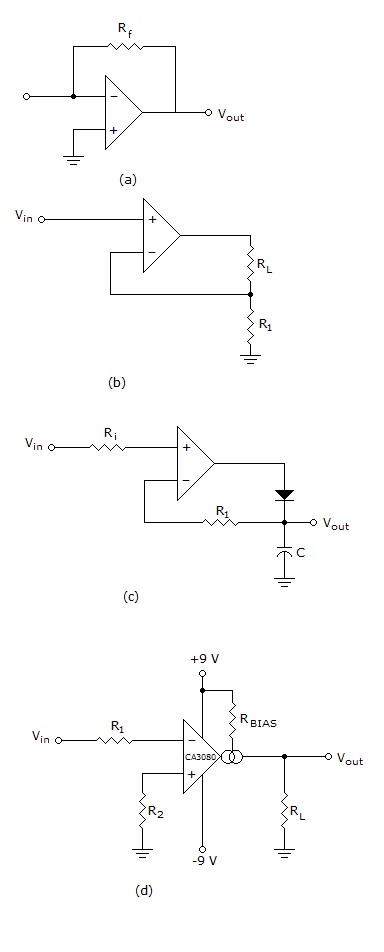
Which circuit is known as a current-to-voltage converter?
Options- A. a
- B. b
- C. c
- D. d Discuss
- 8.
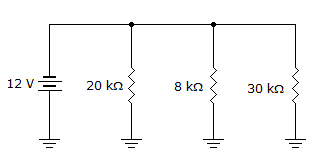
The total resistance in the given circuit is _____.
Options- A. greater than 8 kΩ
- B. 58 kΩ
- C. 4.8 kΩ
- D. greater than 30 kΩ Discuss
- 9.
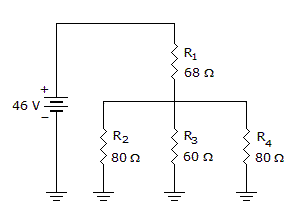
The total resistance in the given circuit can be found using the formula:
RT = R1 + R2 || R3 || R4.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. In a dc circuit, the only conversion of energy to heat is in the inductance of the coil itself.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 46.7°
Correct Answer: self-adjusting
Correct Answer: 11 V
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: The batteries are series-opposing and the total source voltage equals 3 V.
Correct Answer: a
Correct Answer: 4.8 kΩ
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
