Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Magnetism and Electromagnetism See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A Hall effect sensor
Options- A. exists only in theory
- B. is a noncontacting magnetic sensor
- C. can operate only a few times before failure
- D. produces very large voltages
- Correct Answer
- is a noncontacting magnetic sensor
- 1.
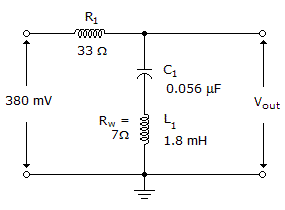
The output voltage is _____ at the resonant frequency in the given circuit.
Options- A. 0 mV
- B. 31.4 mV
- C. 66.5 mV
- D. 380 mV Discuss
- 2. The control bus and memories share a bidirectional bus in a typical microprocessor system.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3.
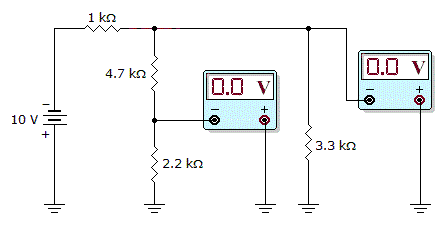
Which circuit fault do the meter readings in the given figure indicate?
Options- A. The 1 kΩ resistor is shorted.
- B. The 4.7 kΩ resistor is shorted.
- C. The 2.2 kΩ resistor is shorted.
- D. The 3.3 kΩ resistor is shorted. Discuss
- 4. Germanium is the most widely used semiconductor material because of its stability at high temperatures.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. What do variable capacitors use for dielectric?
Options- A. ceramic, electrolytic, mica, or paper
- B. air, ceramic, mica, or plastic
- C. ceramic, paper, plastic, or mica
- D. mica, ceramic, plastic, or electrolytic Discuss
- 6. During a current change, the ability of a conductor to produce counter emf within itself is called:
Options- A. back emf
- B. self-induction
- C. a henry
- D. impedance Discuss
- 7. Holding current for an SCR is best described as
Options- A. the minimum current required for turn-off
- B. the current required before an SCR will turn on
- C. the amount of current required to maintain conduction
- D. the gate current required to maintain conduction Discuss
- 8. Power is measured in units of:
Options- A. joules x charge
- B. joules/work
- C. joules x voltage
- D. joules/time Discuss
- 9. Adding in binary, the decimal values 26 + 27 will produce a sum of:
Options- A. 111010
- B. 110110
- C. 110101
- D. 101011 Discuss
- 10. Pulse-triggered flip-flops are also called _________ flip-flops.
Options- A. master-slave
- B. postponed
- C. level
- D. edge Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 66.5 mV
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: The 3.3 kΩ resistor is shorted.
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: air, ceramic, mica, or plastic
Correct Answer: self-induction
Correct Answer: the amount of current required to maintain conduction
Correct Answer: joules/time
Correct Answer: 110101
Correct Answer: master-slave
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
