Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Diodes and Applications See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
In a power supply diagram, which block indicates a smooth dc output?
Options- A. transformer
- B. filter
- C. rectifier
- D. regulator
- Correct Answer
- regulator
- 1. What is the total current?
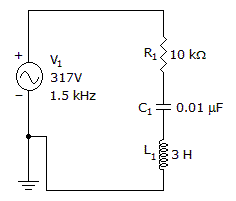
Options- A. 15.6 mA
- B. 17.8 mA
- C. 21.9 mA
- D. 26.0 mA Discuss
- 2. This circuit is a low-pass filter.
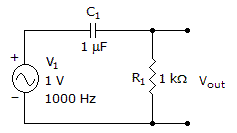
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. If the output of an RC integrator is zero volts, the capacitor might be open.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. A ___ capacitor allows ac signals to pass while blocking dc signals.
Options- A. filter
- B. bypass
- C. decoupling
- D. coupling Discuss
- 5. What happens to total resistance in a circuit with parallel resistors if one of them opens?
Options- A. It increases.
- B. It halves.
- C. It remains the same.
- D. It decreases. Discuss
- 6. If we double the number of bits in our digital representation of a number from 4 to 8 bits, we double the relative accuracy of the conversion from digital to analog.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. Attaching a 6 kΩ load to a voltage divider will cause a smaller decrease in the output voltage than will attaching a 5 kΩ load.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. An ammeter is connected in ______ with the branch resistor to measure branch current, and in ______ with the voltage supply to measure total parallel circuit current.
Options- A. parallel, series
- B. series, parallel
- C. series, series
- D. parallel, parallel Discuss
- 9. The relative accuracy of a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) is determined by settling time.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. The output phase for a transformer is:
Options- A. in phase with the input
- B. out of phase with the input
- C. dependent on the direction of the primary and secondary windings
- D. dependent on the frequency of the primary source Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 15.6 mA
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: coupling
Correct Answer: It increases.
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: series, series
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: dependent on the direction of the primary and secondary windings
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
