Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Inductors See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Faraday's law states that the:
Options- A. direction of the induced voltage produces an opposition
- B. direction of an induced current produces an aiding effect
- C. emf depends on the rate of cutting flux
- D. emf is related to the direction of the current
- Correct Answer
- emf depends on the rate of cutting flux
- 1. As a generator armature passes the 270 degree point, the induced voltage is:
Options- A. at maximum negative
- B. between maximum negative and zero
- C. at maximum positive
- D. between zero and maximum positive Discuss
- 2. In a B-H curve, magnetizing force is equal to:
Options- A.
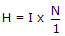
- B. H = I × N
- C. ampere-turns per weber
- D. webers per square meter Discuss
- 3. When a transformer secondary lead has been connected to a middle loop that is not an end connector, it is called a:
Options- A. multiple-tapped secondary
- B. center-tapped secondary
- C. multiple winding secondary
- D. single winding secondary Discuss
- 4. What is the impedance of a 1 kHz series RL circuit when R and XL are both 1000 ohms?
Options- A. 500 ohms
- B. 1000 ohms
- C. 1414 ohms
- D. 2000 ohms Discuss
- 5. A turns ratio of 5 for a transformer implies:
Options- A. more primary turns than secondary turns
- B. more secondary current than primary current
- C. larger source impedance than load impedance
- D. more secondary turns than primary turns Discuss
- 6. What happens when moving expanding lines of force encounter a conductor?
Options- A. Current increases.
- B. Voltage is induced.
- C. Resistance is reduced.
- D. Power is increased. Discuss
- 7. Find VR and VL.
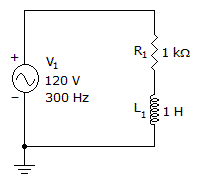
Options- A. VR = 41.6 V, VL = 78.4 V
- B. VR = 48 V, VL = 110 V
- C. VR = 56 V, VL = 106 V
- D. VR = 60 V, VL = 60 V Discuss
- 8. Faraday's law states that the:
Options- A. direction of the induced voltage produces an opposition
- B. direction of an induced current produces an aiding effect
- C. emf depends on the rate of cutting flux
- D. emf is related to the direction of the current Discuss
- 9. A transformer is used:
Options- A. to couple electric energy from one dc circuit to another
- B. to couple electric energy from an ac circuit to a dc circuit
- C. to couple electric energy from a dc circuit to an ac circuit
- D. to couple electric energy from one ac circuit to another Discuss
- 10. The time required for one weber of flux to cut a conductor and produce one volt is:
Options- A. one revolution
- B. one second
- C. one millisecond
- D. four revolutions Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: at maximum negative
Correct Answer:
Correct Answer: center-tapped secondary
Correct Answer: 1414 ohms
Correct Answer: more secondary turns than primary turns
Correct Answer: Voltage is induced.
Correct Answer: VR = 56 V, VL = 106 V
Correct Answer: emf depends on the rate of cutting flux
Correct Answer: to couple electric energy from one ac circuit to another
Correct Answer: one second
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
