Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Semiconductor Memory See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Which of the following RAM timing parameters determine(s) its operating speed?
Options- A. tacc
- B. taa and tacs
- C. t1 and t3
- D. trc and twc
- Correct Answer
- t1 and t3
- 1.
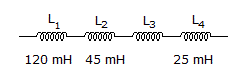
The inductance value of L3 in the given figure is _____ if the total inductance is 340 mH.
Options- A. 150 mH
- B. 220 mH
- C. 295 mH
- D. 315 mH Discuss
- 2. When considering conventional current versus electron current flow:
Options- A. electron current flow came first
- B. protons move in conventional current flow
- C. conventional current flow came first
- D. the direction of current is the same in both methods Discuss
- 3. What type of resistors have a tolerance rating of 5% or greater?
Options- A. precision
- B. SIP
- C. general-purpose
- D. wirewound Discuss
- 4. The resistivity of copper is:
Options- A. 9.9 Ω
- B. 10.7 Ω
- C. 16.7 Ω
- D. 17.0 Ω Discuss
- 5. A transformer turns ratio of ________ will be needed to match an output impedance of 5 kΩ to an 8 Ω speaker.
Options- A. 5:1
- B. 8:1
- C. 25:1
- D. 625:1 Discuss
- 6.
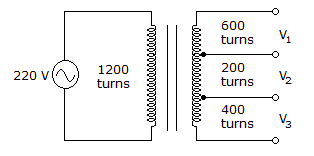
The voltage V2 is _____ in the given circuit.
Options- A. 36.7 V
- B. 73.3 V
- C. 110 V
- D. 220 V
- 7.

When the south poles of two bar magnets are brought close together, there will be a force of attraction.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8. The output of a differentiator could be considered a spike when the input pulse width is much longer than 5 time constants.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. An AND gate and two INVERTERs can be connected to act as a basic decoder.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. The basic difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker is
Options- A. a fuse is slower
- B. a fuse is reusable
- C. a circuit breaker is reusable
- D. a circuit breaker is more reliable Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 150 mH
Correct Answer: conventional current flow came first
Correct Answer: general-purpose
Correct Answer: 10.7 Ω
Correct Answer: 25:1
Correct Answer: 36.7 V
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: a circuit breaker is reusable
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
