Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Semiconductor Memory See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A computerized self-diagnostic for a ROM test uses:
Options- A. the check-sum method
- B. a ROM listing
- C. ROM comparisons
- D. a checkerboard test
- Correct Answer
- the check-sum method
- 1.
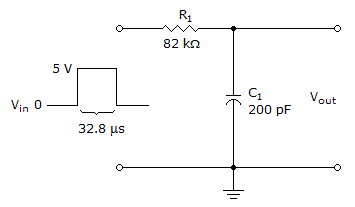
The given circuit is an
Options- A. RL integrator
- B. RC differentiator
- C. RL differentiator
- D. RC integrator Discuss
- 2. The main purpose of an instrumentation amplifier is to amplify small signals riding on large common-mode voltages.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. The symbol hfe is the same as:
Options- A.
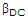
- B.
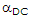
- C. hi-fi
- D.
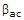 Discuss
Discuss
- 4. The Schmitt trigger is a two-state device that is used for:
Options- A. pulse shaping
- B. peak detection
- C. input noise rejection
- D. filtering Discuss
- 5. Convert the decimal number 151.75 to binary.
Options- A. 10000111.11
- B. 11010011.01
- C. 00111100.00
- D. 10010111.11 Discuss
- 6. What happens to the parallel output word in an asynchronous binary down counter whenever a clock pulse occurs?
Options- A. The output word decreases by 1.
- B. The output word decreases by 2.
- C. The output word increases by 1.
- D. The output word increases by 2. Discuss
- 7. With a JFET, a ratio of output current change against an input voltage change is called:
Options- A. transconductance
- B. siemens
- C. resistivity
- D. gain Discuss
- 8. ?1.2 V, +15 V, and ?6 V batteries are connected in series. The magnitude of total voltage is _________.
Options- A. 7.8 V
- B. 10.2 V
- C. 22.2 V
- D. 1.3 V Discuss
- 9. As frequency decreases in a parallel RL circuit the impedance also decreases.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. The frequency of a crystal is dependent on how much voltage is applied to activate it.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: RC integrator
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer:
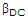
Correct Answer: pulse shaping
Correct Answer: 10010111.11
Correct Answer: The output word decreases by 1.
Correct Answer: transconductance
Correct Answer: 7.8 V
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
