Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Programmable Logic Devices (PLD) See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The difference between a PLA and a PAL is:
Options- A. the PLA has a programmable OR plane and a programmable AND plane, while the PAL only has a programmable AND plane
- B. the PAL has a programmable OR plane and a programmable AND plane, while the PLA only has a programmable AND plane
- C. the PAL has more possible product terms than the PLA
- D. PALs and PLAs are the same thing.
- Correct Answer
- the PLA has a programmable OR plane and a programmable AND plane, while the PAL only has a programmable AND plane
- 1. A(n) ________ amplifier is used if the application requires a high sensitivity to low-level signals and protection from high-voltage associated circuits.
Options- A. basic instrumentation
- B. operational transconductance
- C. log/antilog amplifier
- D. isolation Discuss
- 2. Integrated-injection logic offers high component density and is easier to fabricate than TTL.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. One oscilloscope selector knob that allows the major and minor divisions of the graticule to be used to determine a signal amplitude value is called the:
Options- A. time/cm control
- B. position control
- C. intensity control
- D. volts/cm control Discuss
- 4. What is the name of a device used to directly measure the frequency of a periodic wave?
Options- A. oscilloscope
- B. frequency meter or counter
- C. audio frequency generator
- D. radio frequency generator Discuss
- 5. When matching polarity connections have been made and the potential difference (PD) is above 0.7 V, the diode is considered to be:
Options- A. not working
- B. forward biased
- C. reverse biased
- D. an open switch Discuss
- 6. What does Faraday's law concern?
Options- A. a magnetic field in a coil
- B. a magnetic field cutting a conductor
- C. a magnetic field hystersis
- D. a magnetic field in a conductor Discuss
- 7. In order to sustain oscillations in a feedback oscillator, the gain should be _________ so the product of Av × B equals_______.
Options- A. reduced, one
- B. reduced, less than one
- C. increased, more than one
- D. increased, much greater than one Discuss
- 8. The dc current through each diode in a bridge rectifier equals:
Options- A. the load current
- B. half the dc load current
- C. twice the dc load current
- D. one-fourth the dc load current Discuss
- 9. What is the percent of regulation if Vnl = 20 V and Vfl = 19.8 V?
Options- A. 0%
- B. 1%
- C. .1%
- D. 5% Discuss
- 10. The impedance is 1177 Ω.
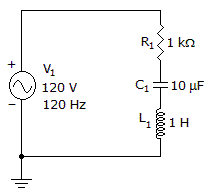
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: isolation
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: volts/cm control
Correct Answer: frequency meter or counter
Correct Answer: forward biased
Correct Answer: a magnetic field cutting a conductor
Correct Answer: reduced, one
Correct Answer: the load current
Correct Answer: 1%
Correct Answer: True
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
