Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Thyristors and Tranducers See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A TRIAC:
Options- A. can trigger only on positive gate voltages
- B. can trigger only on negative gate voltages
- C. cannot be triggered with gate voltages
- D. can be triggered by either a positive or a negative gate voltage
- Correct Answer
- can be triggered by either a positive or a negative gate voltage
- 1. In digital electronic circuits, information is first converted to a coded group of pulses.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. Displacement, velocity, and acceleration can all be measured by using specific motion transducers.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. Another name for "fundamental units" is
Options- A. base units
- B. atoms
- C. the metric system
- D. letter symbols Discuss
- 4. If the current drawn in the secondary of a transformer increases, the power in the primary should remain the same.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. If a current of 40 mA flows through a series circuit consisting of a 0.4 µF capacitor and a resistor in series with a 4 kHz, 40 Vac source, what is the total circuit impedance?
Options- A. 10 Ω
- B. 100 Ω
- C. 1 k Ω
- D. 1 M Ω Discuss
- 6. A multiplexer is a device that chooses which output to send an input to by means of select lines.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. When the output of a standard TTL gate is HIGH, it can ___________________.
Options- A. sink 16 mA of current from the attached input gates
- B. source 400 µA of current to no more than 10 attached gates
- C. source 16 mA of current to no more than 10 attached gates
- D. sink a maximum of 400 µA from no more than 10 load gates Discuss
- 8. What is another name for a one-shot?
Options- A. monostable
- B. bistable
- C. astable
- D. tristable Discuss
- 9.
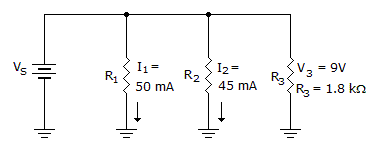
What does RT equal in the given circuit?
Options- A. 90 Ω
- B. 180 Ω
- C. 200 Ω
- D. 1.8 kΩ Discuss
- 10. Resistance in a series circuit will:
Options- A. control the voltage
- B. double the current
- C. halve the power
- D. oppose current Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: base units
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: 1 k Ω
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: source 400 µA of current to no more than 10 attached gates
Correct Answer: monostable
Correct Answer: 90 Ω
Correct Answer: oppose current
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
