Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Ohm's Law See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Energy is defined as the ability to
Options- A. produce heat
- B. produce light
- C. produce sound
- D. All of the above
- Correct Answer
- All of the above
- 1.
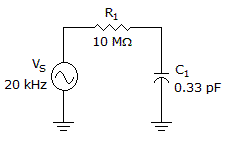
Calculate the phase angle in the given circuit.
Options- A. 0°
- B. 90°
- C. 22.52°
- D. 67.48° Discuss
- 2.
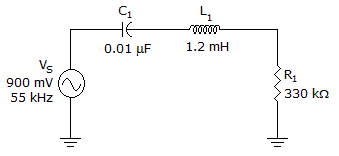
The current lags the voltage in the given circuit.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3. This is a PNP transistor.
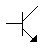
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. What is a circuit that produces short-duration spikes?
Options- A. A trigger pulse generator
- B. An RL integrator
- C. A timing circuit
- D. A pulse waveform-to-dc converter Discuss
- 5. If current through a resistance is halved
Options- A. the resistance is halved
- B. the voltage is halved
- C. the voltage doubles
- D. none of the above Discuss
- 6. With the E-MOSFET, when gate input voltage is zero, drain current is:
Options- A. at saturation
- B. zero
- C. IDSS
- D. widening the channel Discuss
- 7. The device that would best aid in open track detection is a(n) ________.
Options- A. multimeter
- B. current tracer
- C. logic probe
- D. oscilloscope Discuss
- 8. What is the zero-voltage switch used for?
Options- A. To reduce radiation of high frequencies during turn-on of a high current to a load
- B. To control low-voltage circuits
- C. To provide power to a circuit when power is lost
- D. For extremely low-voltage applications Discuss
- 9. In order for a logic probe to operate, its red and black leads must first be connected to a ________.
Options- A. logic clip
- B. HIGH or TRUE signal
- C. power source
- D. logic pulser Discuss
- 10. If the resistance in a circuit with constant voltage increases, the current will
Options- A. increase
- B. decrease
- C. stay the same
- D. Not enough information Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 67.48°
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: A trigger pulse generator
Correct Answer: the voltage is halved
Correct Answer: zero
Correct Answer: current tracer
Correct Answer: To reduce radiation of high frequencies during turn-on of a high current to a load
Correct Answer: power source
Correct Answer: decrease
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
