Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Capacitors See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A practical capacitor
Options- A. is a short to dc
- B. looks like a capacitor in parallel with a resistor
- C. is an open to ac
- D. stores energy in a magnetic field
- Correct Answer
- looks like a capacitor in parallel with a resistor
- 1.
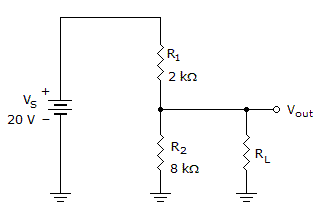
If the load in the given circuit is 80 kΩ , what is the bleeder current?
Options- A. 196 µ A
- B. 1.96 mA
- C. 2 mA
- D. 2.16 mA Discuss
- 2. A thermistor's temperature characteristic is essentially _________.
Options- A. linear
- B. logarithmic
- C. nonlinear
- D. geometric Discuss
- 3. Which resistive component is designed to be temperature sensitive?
Options- A. Thermistor
- B. Rheostat
- C. Potentiometer
- D. Photoconductive cell Discuss
- 4.
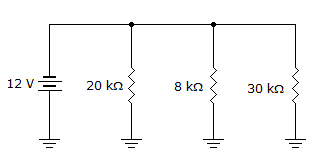
The total current in the given circuit is ___.
Options- A. 2.5 mA
- B. 0.6 mA
- C. 1.5 mA
- D. 0.4 mA Discuss
- 5. If the impedance equals 2 kΩ in a parallel RC circuit, the admittance equals ___.
Options- A. More information is needed in order to find the admittance.
- B. 2 kS
- C. 4 kS
- D. 500 µS Discuss
- 6.
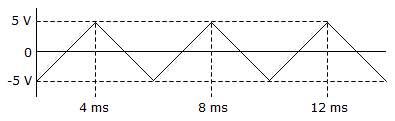
Calculate the positive-going slope of the waveform in the given circuit.
Options- A. 5 V/ms
- B. 2.5 V/ms
- C. 2.5 V/s
- D. 5 V/s Discuss
- 7. A circuit is parallel between two points if ___ between those two points.
Options- A. the voltage divides
- B. more than one current path exists
- C. all resistors are equal
- D. there is only one current path Discuss
- 8. If XL= 100 Ω and R = 100 Ω, then impedance will be
Options- A. 141.4 Ω
- B. 14.14 Ω
- C. 100 Ω
- D. 200 Ω Discuss
- 9. The total resistance is 480 Ω.
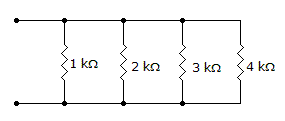
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. A multiplexer is a device that outputs a fixed sequence of binary states on each clock pulse.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 1.96 mA
Correct Answer: logarithmic
Correct Answer: Thermistor
Correct Answer: 2.5 mA
Correct Answer: 500 µS
Correct Answer: 2.5 V/ms
Correct Answer: more than one current path exists
Correct Answer: 141.4 Ω
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright İCuriousTab. All rights reserved.
