Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Capacitors See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The quantity that represents an ideal capacitor dissipating 0 W of power is
Options- A. instantaneous power
- B. true power
- C. reactive power
- D. resistive power
- Correct Answer
- true power
- 1. XL = 2ΠfL
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 2. A voltage is induced across a conductor if it remains absolutely stationary within a magnetic field.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 3.

How much current flows in the circuit in the given circuit?
Options- A. 20 µA
- B. 60 µA
- C. 80 µA
- D. 140 µA Discuss
- 4. The time constant of an inductive circuit is dependent on the circuit's resistance.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. When the output of a tri-state shift register is disabled, the output level is placed in a:
Options- A. float state
- B. LOW state
- C. high impedance state
- D. float state and a high impedance state Discuss
- 6.
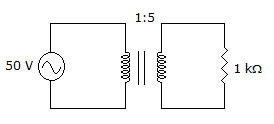
If the load doubled in value in the given circuit, what reflected resistance would the source see?
Options- A. 80 Ω
- B. 400 Ω
- C. 2 kΩ
- D. 10 kΩ Discuss
- 7. In a 20 Vac series RC circuit, if 20 V is read across the resistor and 40 V is measured across the capacitor, the applied voltage is
Options- A. 45 Vac
- B. 50 Vac
- C. 60 Vac
- D. 65 Vac Discuss
- 8. Capacitance is directly proportional to the dielectric constant and the distance between its plates and inversely proportional to the area of the plates.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9. If both inputs are required to be ON for the output to be ON, the gate must be an AND gate.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 10. What circuit has the following frequency response?
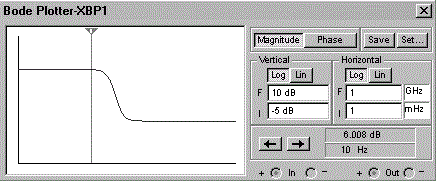
Options- A. bandpass filter
- B. high-pass filter
- C. low-pass filter
- D. integrator Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: 20 µA
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: float state and a high impedance state
Correct Answer: 80 Ω
Correct Answer: 45 Vac
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: low-pass filter
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
