Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Parallel Circuits See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Which component is shorted?
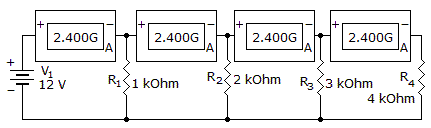
Options- A. R1
- B. R2
- C. R3
- D. R4
- Correct Answer
- R4
- 1. Inaccurate analog-to-digital conversion may be due to ____________.
Options- A. constant analog input voltage
- B. linear ramp usage
- C. intermittent counter inputs
- D. faulty sample-and-hold circuitry Discuss
- 2. The voltage across a 2.2 kΩ resistor is ___ if 3 mA of current is flowing through it.
Options- A. 6.6 V
- B. 7.33 V
- C. 1.4 V
- D. 0.8 V Discuss
- 3. Carbon composition resistors are the most common and the least expensive type of fixed-value resistor.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. The beta of a BJT is the ratio of collector current to emitter current.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. A Wheatstone bridge may be used to determine the value of an unknown resistance.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 6. What is the quality factor?
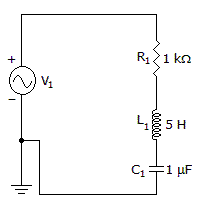
Options- A. 999
- B. 223
- C. 2.2
- D. 0.99 Discuss
- 7. For series ac circuits containing both resistance and inductive reactance, total opposition to current can be found by simply adding ohmic values or oppositions to current.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 8.
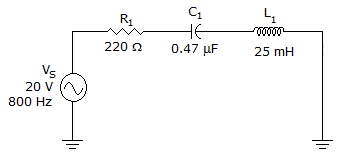
What is the impedance of the circuit in the given circuit?
Options- A. 125.7 Ω
- B. 297.6 Ω
- C. 370.1 Ω
- D. 423.3 Ω Discuss
- 9. What is the band pass (F1 ? F2) of an RLC filter that resonates at 150 kHz and has a coil Q of 30?
Options- A. 100.0 kHz to 155.0 kHz
- B. 147.5 kHz to 152.5 kHz
- C. 295.5 kHz to 4500 kHz
- D. 149,970 Hz to 150,030 Hz Discuss
- 10. An oscillator whose frequency can be controlled by an input "control voltage" is called a(n) ______ .
Options- A. PLL
- B. Schmitt trigger
- C. VCO
- D. S-R latch Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: faulty sample-and-hold circuitry
Correct Answer: 6.6 V
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: 2.2
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: 370.1 Ω
Correct Answer: 147.5 kHz to 152.5 kHz
Correct Answer: VCO
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
