Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Voltage and Current See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
When considering conventional current versus electron current flow:
Options- A. electron current flow came first
- B. protons move in conventional current flow
- C. conventional current flow came first
- D. the direction of current is the same in both methods
- Correct Answer
- conventional current flow came first
- 1. Which coil would be used as a step-up transformer primary if coil number 1 has 100 more turns than coil number 2?
Options- A. The coil windings must be the same.
- B. coil 1
- C. The coil ratio is too small.
- D. coil 2 Discuss
- 2. What is the total inductance assuming no mutual inductance?
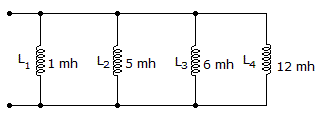
Options- A. 0 mH
- B. 0.69 mH
- C. 12 mH
- D. 24 mH Discuss
- 3. The quality factor of a parallel circuit at resonance is VC/VS or VL/VS.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4.
A magnetic field is produced around a current-carrying conductor.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 5. What is the total opposition to current in a series RC circuit called?
Options- A. impedance
- B. inductance
- C. reactance
- D. resistance Discuss
- 6.
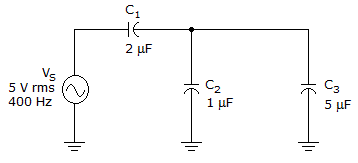
The reactance of C2 is _____ in the given circuit.
Options- A. 66 Ω
- B. 80 Ω
- C. 199 Ω
- D. 398 Ω Discuss
- 7.
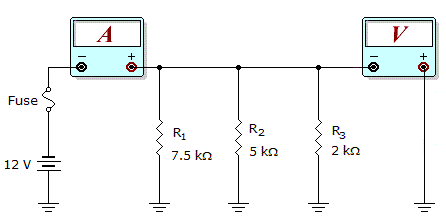
What would these meter readings indicate about the circuit in the given circuit?
Meter Readings: I = 7.6 mA, V = 12 V
Options- A. R1 is open.
- B. R2 is open.
- C. The fuse is open.
- D. The circuit is operating normally. Discuss
- 8. A rectangular wave that has a duty cycle of 50 percent could be called a:
Options- A. c wave
- B. sawtooth wave
- C. square wave
- D. triangle wave Discuss
- 9. If the current in a circuit equals 0 A, it is likely that the
Options- A. voltage is too high
- B. resistance is too low
- C. circuit has a short
- D. circuit is open Discuss
- 10. Capacitors are often used as filters.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: coil 2
Correct Answer: 0.69 mH
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: True
Correct Answer: impedance
Correct Answer: 398 Ω
Correct Answer: R2 is open.
Correct Answer: square wave
Correct Answer: circuit is open
Correct Answer: True
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
