Discussion
Home ‣ Electronics ‣ Voltage and Current See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
A basic electric circuit is made up of what components?
Options- A. A load, a resistor, and a conductive path for current
- B. A voltage source, a load, and a conductive path for current
- C. A voltage source, a conductive path for current, and a battery
- D. A conductive path for current, a battery, and a copper wire
- Correct Answer
- A voltage source, a load, and a conductive path for current
- 1.
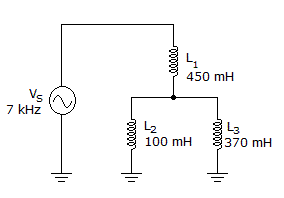
The total inductive reactance is ___ in the given circuit.
Options- A. 3.5 kΩ
- B. 4.4 kΩ
- C. 16.3 kΩ
- D. 23.3 kΩ Discuss
- 2. If a 5 V, 60 Hz voltage is applied to a 4.7 µF capacitor, the circuit current will be ______ .
Options- A. 0.886 mA
- B. 8.86 mA
- C. 8.86 µA
- D. 88.6 µA Discuss
- 3. ASCII codes are used strictly for representing the letters in the alphabet.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 4. The precision rectifier circuit is designed to _________.
Options- A. rectify waveforms with very large voltage swings
- B. rectify waveforms with very small voltage swings
- C. rectify precision waveforms
- D. amplify and rectify waveforms Discuss
- 5. The ___ oscillator takes advantage of the piezoelectric effect.
Options- A. crystal
- B. Hartley
- C. Colpitts
- D. RC Discuss
- 6. When inductive and capacitive reactance are present in the same series circuit, the magnitude of the total reactance is equal to the sum of the magnitudes of the individual reactances.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 7. When the resistance is greater than the capacitive reactance in a series RC circuit, the phase angle is ___.
Options- A. 0°
- B. between 0° and 45°
- C. between 45° and 90°
- D. 45° Discuss
- 8. The resonant frequency fo is 19 kHz.
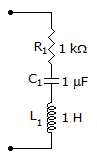
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
- 9.
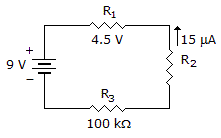
In the given circuit, R1 equals _____.
Options- A. 100 kΩ
- B. 200 kΩ
- C. 300 kΩ
- D. More information is needed to find R1. Discuss
- 10. The ability of a material to maintain a magnetized state (without the presence of a magnetizing force) is called retentivity.
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 23.3 kΩ
Correct Answer: 8.86 mA
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: rectify waveforms with very small voltage swings
Correct Answer: crystal
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: between 0° and 45°
Correct Answer: False
Correct Answer: 300 kΩ
Correct Answer: True
Comments
There are no comments.More in Electronics:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
