Power Electronics problems
- 1. A cycloconverter uses
Options- A. natural commutation
- B. forced commutation
- C. either natural or forced commutation
- D. both natural and forced commutation together Discuss
Correct Answer: either natural or forced commutation
- 2. In a half bridge inverter circuit fed by a battery of voltage V, the rms value of fundamental component of output voltage is
Options- A. 2 V
- B.
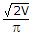
- C.
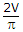
- D.
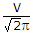 Discuss
Discuss
Correct Answer:
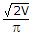
- 3. A step down cycloconverter has an input frequency f. If it uses natural commutation, the output frequency
Options- A. must be a sub-multiple of input frequency
- B. can be any frequency
- C. must be an even sub-multiple of input frequency
- D. must be an odd sub-multiple of input frequency Discuss
Correct Answer: must be a sub-multiple of input frequency
- 4. Assertion (A): SUS is a PUT and avalanche diode connected between gate and cathode
Reason (R): SBS has two SUS inbuilt together and connected in anti-parallel
Options- A. Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A
- B. Both A and R correct but R is not correct explanation of A
- C. A is correct but R is wrong
- D. A is wrong but R is correct Discuss
Correct Answer: Both A and R correct but R is not correct explanation of A
- 5. Which statement is correct?
Options- A. BJT and MOSFET are current controlled devices
- B. BJT is voltage controlled and MOSFET is current controlled device
- C. BJT and MOSFET are voltage controlled devices
- D. BJT is current controlled and MOSFET is voltage controlled device Discuss
Correct Answer: BJT is current controlled and MOSFET is voltage controlled device
- 6. A class E chopper
Options- A. can operate in second quadrant only
- B. can operate in first or third quadrant
- C. can operate in all the four quadrants
- D. can operate in either second or third quadrant Discuss
Correct Answer: can operate in all the four quadrants
- 7. Which of the following commutation methods is the overall circuit under damped?
Options- A. Class A
- B. Class B
- C. Class C
- D. Both class A and Class B Discuss
Correct Answer: Both class A and Class B
- 8. In a full bridge single phase inverter feeding RLC load
Options- A. one thyristor and one diode conduct simultaneously
- B. two thyristors conduct simultaneously
- C. two thyristors or two diodes conduct simultaneously
- D. four thyristors conduct simultaneously Discuss
Correct Answer: two thyristors or two diodes conduct simultaneously
- 9. In a parallel inverter the turn off time tq of thyristor and values of commutating elements L and C are related as
Options- A. tq = pLC
- B. tq =
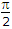 LC
LC - C. tq =
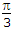 LC
LC - D. tq =
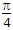 LC
Discuss
LC
Discuss
Correct Answer: tq =
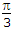 LC
LC - 10. A single phase full wave regulator feeds a resistive load. The firing angle of thyristors is 90°. The input power factor is
Options- A. 1
- B. 0.707 lagging
- C. 0.5 lagging
- D. 0.2 lagging Discuss
Correct Answer: 0.707 lagging
More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
