Microwave Communication problems
- 1. In which mode of circular waveguide does the attenuation continuously decrease as frequency is increased?
Options- A. TE01
- B. TE11
- C. TE05
- D. TE21 Discuss
Correct Answer: TE01
- 2. As regards rectangular and circular waveguides
Options- A. both have infinite set of TE and TM modes
- B. rectangular waveguide has infinite TE and TM modes but not the circular waveguide
- C. circular waveguide has infinite TE and TM modes but not the rectangular waveguide
- D. none of the above Discuss
Correct Answer: both have infinite set of TE and TM modes
- 3. Consider the following statements about instrument landing system of aircraft
- It ensures correct landing under conditions of low visibility.
- It consists of runaway localizer, glide path equipment and marker beacons.
- It is basically a blind landing system.
Options- A. All
- B. 1 and 2 only
- C. 1 and 3 only
- D. 2 only Discuss
Correct Answer: All
- 4. For air filled circular waveguides
Options- A. the attenuation due to imperfect conducting walls is negligible
- B. the attenuation due to imperfect dielectric is negligible
- C. both the attenuation i.e. due to imperfect conducting walls and due to imperfect dielectric are significant
- D. the total attenuation is almost zero Discuss
Correct Answer: the attenuation due to imperfect dielectric is negligible
- 5. The attenuation characteristics of a loaded line is similar to that of
Options- A. low pass filter
- B. high pass filter
- C. band pass filter
- D. band stop filter Discuss
Correct Answer: band stop filter
- 6. In a microwave coaxial cable the inner conductor radius is a and inner radius of outside conductor is b. For TE11 mode the cut off wavelength is about
Options- A. a + b
- B. p(a + b)
- C. pa
- D. pb Discuss
Correct Answer: p(a + b)
- 7. Radar is essentially an echo ranging system
Options- A. True
- B. False Discuss
Correct Answer: True
- 8. A directional coupler is used to determine
Options- A. rv
- B. rv and VSWR
- C. L and C
- D. wave velocity Discuss
Correct Answer: rv and VSWR
- 9. A TR (transmitter receiver) tube has
Options- A. low loss for low power signals and high
- B. high loss for low power signals and low loss for high level signal
- C. low loss for both low level and high level signals
- D. high loss for both low level and high level signals Discuss
Correct Answer: low loss for low power signals and high
- 10. Assertion (A): In TE10 mode the cutoff frequency of rectangular waveguide is
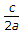 where a is the broad dimension and c is velocity of light.
where a is the broad dimension and c is velocity of light.Reason (R): TE10 mode is the dominant mode in rectangular waveguide.
Options- A. Both A and R are correct and R is correct explanation of A
- B. Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A
- C. A is correct but R is wrong
- D. A is wrong but R is correct Discuss
Correct Answer: Both A and R are correct but R is not correct explanation of A
More in Electronics and Communication Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
