Highway Engineering problems
- 1. Stability of hill slopes depends upon
Options- A. nature of the slope
- B. angle of the slope
- C. geological conditions
- D. ground water conditions
- E. all the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: all the above.
- 2. If N is the algebraic difference of grades, S is the minimum sight distance in metres, the length (L) of a summit curve is
Options- A.
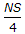
- B.
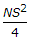
- C.
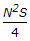
- D.
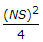
- E. none of these. Discuss
Correct Answer:
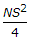
- 3. If the number of lanes on the carriageway of a road is more than two, the total width of lane ways is equal to 3.0 m
Options- A. + 0.60 m
- B. + 0.70 m
- C. + 0.80 xn
- D. + 0.90 m
- E. + 1.50 m Discuss
Correct Answer: + 0.70 m
- 4. Along high ways confirmatory route markers are generally fixed
Options- A. before the crossing on the left side
- B. after the crossing on the left side
- C. before the crossing on the right side
- D. after the crossing on the right side. Discuss
Correct Answer: after the crossing on the left side
- 5. For Indian conditions, the water bound macadam roads, are suitable if daily traffic does not exceed
Options- A. 2000 tonnes
- B. 2500 tonnes
- C. 3000 tonnes
- D. 3500 tonnes Discuss
Correct Answer: 2000 tonnes
- 6. The desirable camber for straight cement concrete roads, is
Options- A. 1 in 33 to 1 in 25
- B. 1 in 40 to 1 in 33
- C. 1 in 150 to 1 in 140
- D. 1 in 160 to 1 in 140
- E. none of these. Discuss
Correct Answer: 1 in 160 to 1 in 140
- 7. If d is the thickness of a concrete pavement, the equivalent radius b of resisting section for an interior loading, is
Options- A. b = 0.6 + d2 - 0.675 d
- B. b = 1.6 + d2 + 0.675 d
- C. b = 1.6 + d2 - 3.675 d
- D. b = 1.6 + d2 - 0.675 d Discuss
Correct Answer: b = 1.6 + d2 - 0.675 d
- 8. If N is the algebraic difference of grades, S is the head light beam distance in metres, the length (L) of a valley curve, is
Options- A.
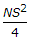
- B.
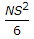
- C.
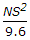
- D.
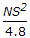
- E.
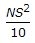 Discuss
Discuss
Correct Answer:
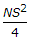
- 9. Selection of the routes, of highways depends upon
Options- A. feasibility of attaining ruling gradient
- B. avoidance of cutting hard rocks
- C. minimum number of bridges
- D. minimum possible length of alignment
- E. all the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: all the above.
- 10. The minimum design speed of various types of highways in plain terrain is the same as the ruling design speed of
Options- A. rolling terrain
- B. mountainous terrain
- C. steep terrain
- D. none of these. Discuss
Correct Answer: rolling terrain
More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
