Highway Engineering problems
- 1. The type of transition curves generally provided on hill roads, is
Options- A. circular
- B. cubic parabola
- C. Lemniscate
- D. spiral. Discuss
Correct Answer: spiral.
- 2. Border Roads Organisation for hilly regions, was formed in
Options- A. 1947
- B. 1954
- C. 1958
- D. 1960
- E. 1962 Discuss
Correct Answer: 1960
Explanation:
The Border Roads Organization (BRO) was conceived and raised in the year 1960 by Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, the great visionary and the first Prime Ministry of India. This was done with the aim of coordinating the speedy development of network of roads in the North and the North Eastern border regions of the country. BRO is regarded as a symbol of nation-building, national integration and an inseparable component in maintaining the security and integrity of the country.
- 3. The minimum ratio of the radii of two circular curves of a compound curve, is kept
Options- A. 1.25
- B. 1.5
- C. 1.75
- D. 2.0 Discuss
Correct Answer: 1.5
- 4. The efficiency of the brakes of a vehicle depends upon
Options- A. condition of road surface
- B. condition of the tyres
- C. presence of the show moisture
- D. all the above. Discuss
Correct Answer: all the above.
- 5. If A is the projected area of a vehicle in square metres, V is speed of the vehicles in kilometres per hour and C is a constant, then the wind resistance R to the moving vehicles, is given by
Options- A. R = CAV
- B. R = CAV2
- C. R = CAV3
- D.
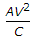
- E. R = C2AV Discuss
Correct Answer: R = CAV2
- 6. If cross slope of a country is 10% to 25%, the terrain is classified as
Options- A. rolling
- B. mountainous
- C. steep
- D. plain. Discuss
Correct Answer: rolling
- 7. A single lane carriage way whenever changes to two-lane carriage way, is affected through a taper of
Options- A. 1 in 10
- B. 1 in 15
- C. 1 in 20
- D. 1 in 15 to 1 in 20 Discuss
Correct Answer: 1 in 15 to 1 in 20
- 8. Design of flexible pavements is based on
Options- A. mathematical analysis
- B. empirical formulae
- C. a compromise of pure theory and pure empirical formula
- D. none of these. Discuss
Correct Answer: a compromise of pure theory and pure empirical formula
- 9. The basic formula for determination of pavement thickness was first suggested by
Options- A. Spanglar
- B. Picket
- C. Kelly
- D. Goldbeck Discuss
Correct Answer: Goldbeck
- 10. Pick up the incorrect statement from the following. The super-elevation on roads is
Options- A. directly proportional to width of pavement
- B. directly proportional to velocity of vehicles
- C. inversely proportional to acceleration due to gravity
- D. inversely proportional to the radius of curvature. Discuss
Correct Answer: directly proportional to velocity of vehicles
More in Civil Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
