Discussion
Home ‣ Chemical Engineering ‣ Furnace Technology See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Overfire burning in a furnace is a phenomenon characterised by
Options- A. supply of excess fuel.
- B. supply of excess air.
- C. burning carbon monoxide and other incombustible in upper zone of furnace by supplying more air.
- D. none of these.
- Correct Answer
- burning carbon monoxide and other incombustible in upper zone of furnace by supplying more air.
- 1. Electrical conductivities of semi-conductors are of the order of __________ ohm/cm.
Options- A. 10-3
- B. 103
- C. 10-15
- D. l015 Discuss
- 2. The frequency response of a dynamic element shows a constant magnitude ratio at all frequencies. The element exhibits a negative phase shift at all frequencies. The absolute value of the phase shift increases linearly with frequency. The element has the transfer function
Options- A. e-?s
- B.
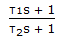
- C.
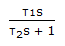
- D.
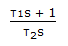 Discuss
Discuss
- 3. Pressure of 0.0001 absolute psi can be measured by __________ gauge.
Options- A. Mcloid
- B. Pirani
- C. thermocouple
- D. none of these Discuss
- 4. The amplitude ratio for the sinusoidal response of a __________ is 1.
Options- A. first order system
- B. second order system
- C. transportation lag
- D. none of these Discuss
- 5. Prime coking coal is always blended with medium or non- coking coal before ear-bonisation
Options- A. to check against its excessive swelling during heating, which may exert high pressure and damage coke oven walls.
- B. because, it alone produces unreactive coke.
- C. both (a) and (b).
- D. neither (a) nor (b). Discuss
- 6. Fluorosis is caused due to the presence of excessive amount of __________ in drinking water.
Options- A. mercury
- B. lead
- C. fluoride
- D. arsenic Discuss
- 7. Liquid argon level in a pressurised storage tank (at 3 kg/cm2 ) is measured by a/an
Options- A. gage glass
- B. external float gage
- C. differential pressure gage
- D. none of these Discuss
- 8. Magnetic flowmeters are generally not used for the velocity/flow measurement of hydrocarbons due to their
Options- A. low thermal conductivity.
- B. low electrical conductivity.
- C. high viscosity index.
- D. low flash point. Discuss
- 9. Pick out the wrong statement.
Options- A. Biological oxygen demand (BOD) is a characteristic and not a constituent of water.
- B. BOD is a measure of the amount of oxygen which will be demanded & used in 5 days by the biological decomposition of the organic matter present in water stream present as food for the living organism.
- C. BOD is expressed in mg/litre (typically, BOD=2.5 mg/litre for potable water).
- D. none of these Discuss
- 10. Ball mills and tube mills with flint or porcelain balls are used for size reduction of
Options- A. asbestos
- B. rubber
- C. non-metallic ores
- D. limestone Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 10-3
Correct Answer: e-?s
Correct Answer: Mcloid
Correct Answer: transportation lag
Correct Answer: both (a) and (b).
Correct Answer: fluoride
Correct Answer: differential pressure gage
Correct Answer: low electrical conductivity.
Correct Answer: none of these
Correct Answer: non-metallic ores
Comments
There are no comments.More in Chemical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
