Discussion
Home ‣ Chemical Engineering ‣ Refractory Technology See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Addition of zircon to silica refractory brick improves its
Options- A. crushing strength
- B. resistance to slag attack
- C. both (a) and (b)
- D. neither (a) nor (b)
- Correct Answer
- resistance to slag attack
- 1. ░API gravity of water at N.T.P. is about
Options- A. 0
- B. 1
- C. 10
- D. 100 Discuss
- 2. Carbon Content by weight in air dried wood may be about __________ percent.
Options- A. 10
- B. 25
- C. 50
- D. 80 Discuss
- 3. Energy produced in the nuclear fission is of the order of __________ MeV.
Options- A. 20
- B. 200
- C. 1000
- D. 2000 Discuss
- 4.
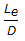 for a Tee (used as elbow, entering run) would be around
for a Tee (used as elbow, entering run) would be around
Options- A. 5
- B. 60
- C. 200
- D. 350 Discuss
- 5. 200 mesh seive size corresponds to __________ microns.
Options- A. 24
- B. 74
- C. 154
- D. 200 Discuss
- 6. Polycaprolactum is also known as
Options- A. nylon-66
- B. nylon-6
- C. teflon
- D. SBR Discuss
- 7. Carbon/hydrogen ratio (by weight) is maximum (out of following) for
Options- A. gasoline
- B. kerosene
- C. light gas oil
- D. heavy fuel oil Discuss
- 8. Salt content in sea water is about __________ percent.
Options- A. 0.5
- B. 1
- C. 3.5
- D. 10 Discuss
- 9. Refractoriness/fusion points of 'superduty' refractories is __________ ░C.
Options- A. 1520-1630
- B. 1630-1670
- C. > 1730
- D. > 2000 Discuss
- 10. Laminar flow of a Newtonion fluid ceases to exist, when the Reynolds number exceeds
Options- A. 4000
- B. 2100
- C. 1500
- D. 3000 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 10
Correct Answer: 50
Correct Answer: 200
Correct Answer: 60
Correct Answer: 74
Correct Answer: nylon-6
Correct Answer: gasoline
Correct Answer: 3.5
Correct Answer: > 1730
Correct Answer: 2100
Comments
There are no comments.More in Chemical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ęCuriousTab. All rights reserved.
