Discussion
Home ‣ Chemical Engineering ‣ Nuclear Power Engineering See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
Energy produced in the nuclear fission is of the order of __________ MeV.
Options- A. 20
- B. 200
- C. 1000
- D. 2000
- Correct Answer
- 200
- 1. In packed absorption tower, onset of flooding usually occurs at a pressure drop of about __________ mm of water column per metre height of packing.
Options- A. 25-50
- B. 50-75
- C. 200-250
- D. 750-1000 Discuss
- 2. With the increase of temperature, the Col-burn jH factor
Options- A. increases.
- B. decreases.
- C. remains unchanged.
- D. may increase or decrease ; depending on temperature. Discuss
- 3. The type of stress developed in a metallic bar on subjecting it to a change in temperature without allowing it to be deformed is __________ stress.
Options- A. shear
- B. tensile
- C. compressive
- D. thermal Discuss
- 4. Utilities cost in the operation of chemical process plant comes under the
Options- A. plant overhead cost
- B. fixed charges
- C. direct production cost
- D. general expenses Discuss
- 5. The velocity profile for turbulent flow through a closed conduit is
Options- A. logarithmic
- B. parabolic
- C. hyperbolic
- D. linear Discuss
- 6. The necessary wall thickness for a metallic storage vessel is a function of the
Options- A. ultimate tensile strength (or yield point) of the material and operating temperature.
- B. operating pressure and welding/joint efficiency.
- C. diameter of the vessel.
- D. all (a); (b) and (c). Discuss
- 7. Smoker's equation for the calculation of number of equilibrium stages in a continuous binary distillation column is used, when the
Options- A. relative volatility is close to one (e.g., separation of close boiling isomers).
- B. feed is not at its bubble point.
- C. number of equilibrium stages in only stripping section is to be calculated.
- D. number of equilibrium stages required is likely to be very small. Discuss
- 8. Friction factor for turbulent flow in a new pipe is given by
Options- A.
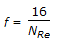
- B.
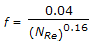
- C. f = 0.22 NRe0.5
- D.
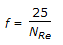 Discuss
Discuss
- 9. In a bag filter, the pressure drop increases directly as the
Options- A. density of the gas, but is independent of the viscosity of the gas.
- B. density of the gas and inversely as viscosity of the gas.
- C. viscosity of the gas and inversely as density of the gas.
- D. none of these. Discuss
- 10. Gum formation in stored gasoline is mainly due to the
Options- A. alkylation of unsaturates.
- B. presence of sulphur.
- C. oxidation & polymerisation of unsaturates.
- D. higher aromatic content. Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 50-75
Correct Answer: increases.
Correct Answer: thermal
Correct Answer: direct production cost
Correct Answer: logarithmic
Correct Answer: all (a); (b) and (c).
Correct Answer: relative volatility is close to one (e.g., separation of close boiling isomers).
Correct Answer:
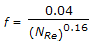
Correct Answer: density of the gas and inversely as viscosity of the gas.
Correct Answer: presence of sulphur.
Comments
There are no comments.More in Chemical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
