Discussion
Home ‣ Chemical Engineering ‣ Stoichiometry See What Others Are Saying!
- Question
The forces causing the vaporisation of liquid are derived from the Kinetic energy of translation of its molecules. The heat of vaporisation
Options- A. increases with pressure rise.
- B. decreases with increasing pressure.
- C. becomes zero at the critical point.
- D. both (b) & (c).
- Correct Answer
- both (b) & (c).
- 1. Cellulose content in bomboo fibre is about __________ percent.
Options- A. 10
- B. 20
- C. 50
- D. 85 Discuss
- 2. Gold ore concentration is mostly done using
Options- A. jigging
- B. tabling
- C. froth floatation
- D. elutriation Discuss
- 3. Vapor pressure of water at 100°C is about __________ bar.
Options- A. 0.1013
- B. 1.013
- C. 10.13
- D. 101.3 Discuss
- 4. P2O5 content in triple superphosphate is about __________ percent.
Options- A. 42-50
- B. 15-20
- C. 85-90
- D. 70-75 Discuss
- 5. For a cylindrical shell, (subject to the thickness of uppermost course being more than the minimum for diaofthe tank in question), the thickness of the courses of shell
Options- A. decreases upwards.
- B. increases upwards.
- C. remains same throughout.
- D. may decrease or increase upwards depending upon whether vacuum or positive pressure would be maintained inside the shell. Discuss
- 6. Water is flowing through a series of four tanks and getting heated as shown in figure. It is desired to design a cascade control scheme for controlling the temperature of water leaving the tank 4 as there is a disturbance in the temperature of a second stream entering the tank 2. Select the best place to take the secondary measurement for the second loop.
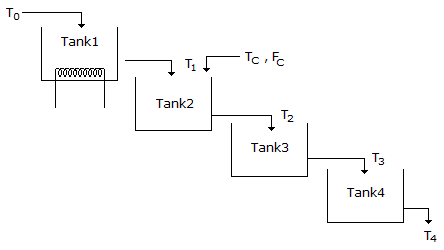
Options- A. Tank 1
- B. Tank 2
- C. Tank 3
- D. Tank 4 Discuss
- 7. The gas which contributes maximum to the heating value of natural gas is
Options- A. CO
- B. CO2
- C. H2
- D. CH4 Discuss
- 8. Pick out the wrong unit conversion.
Options- A. l kgf= 9.8 Newton.
- B. 1 stoke = 1 m2/second.
- C. 1 Pascal second = 10 poise.
- D. 1 ppm = 1 ml/m3 = 1 mg/kg. Discuss
- 9. Styrene butadiene rubber is commercially manufactured by
Options- A. bulk polymerisation
- B. suspension polymerisation
- C. solution polymerisation
- D. emulsion polymerisation Discuss
- 10. Fast breeder nuclear reactors using enriched uranium as fuel may contain upto a maximum of __________ percent of U-235 (i.e. fissile material).
Options- A. 15
- B. 45
- C. 65
- D. 85 Discuss
More questions
Correct Answer: 50
Correct Answer: tabling
Correct Answer: 1.013
Correct Answer: 42-50
Correct Answer: decreases upwards.
Correct Answer: Tank 3
Correct Answer: CH4
Correct Answer: 1 stoke = 1 m2/second.
Correct Answer: emulsion polymerisation
Correct Answer: 85
Comments
There are no comments.More in Chemical Engineering:
Programming
Copyright ©CuriousTab. All rights reserved.
